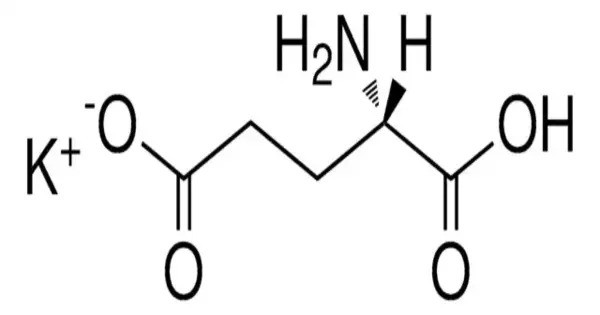
Monopotassium glutamate (MPG) is the compound with formula KC5H8NO4. It is a chemical compound that is a potassium salt of glutamic acid, similar to monosodium glutamate (MSG). It is a potassium salt of glutamic acid. It is used as a flavor enhancer in food, providing an umami taste.
It has the E number E622 and is used in foods as a flavor enhancer. It is a non-sodium MSG alternative. It consists of the glutamate anion and a potassium cation (K⁺), replacing sodium in MSG.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C5H8KNO4
- Molar mass: 185.220 g·mol−1
- Appearance: White crystalline powder
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water
- pH (1% solution): ~7
- Melting Point: Decomposes on heating
- Taste: Umami (savory)
- Stability: Stable under normal conditions
Natural Occurrence
Monopotassium glutamate itself is not commonly found in nature in pure form, but glutamic acid and its salts (like MPG) are naturally present in:
- Protein-rich foods (as glutamate): Seaweed (e.g., kombu), Aged cheeses, Tomatoes, Mushrooms, Meat and fish
- Fermented foods: Soy sauce, Miso, Fermented bean paste
In these sources, potassium salts may naturally occur, but industrial MPG is synthesized by neutralizing glutamic acid with potassium hydroxide (KOH).
Use in Food
- MPG is used as a flavor enhancer, just like MSG.
- It provides the umami taste — a savory flavor common in meats, broths, and mushrooms.
- It’s sometimes used as a low-sodium alternative to MSG, especially for those needing to limit sodium intake.
Applications Beyond Food
- Occasionally used in biochemical research or nutritional formulations.
- Acts as a source of potassium and glutamate, which are essential for cellular functions.
Regulation
- Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) when used in reasonable amounts.
- Overconsumption can lead to the same concerns as MSG (e.g., “Chinese Restaurant Syndrome”), although evidence is limited.
- High potassium intake may be a concern for individuals with kidney problems.
Health & Safety
Generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory agencies when consumed in typical amounts. Like MSG, it may cause sensitivity reactions in a small subset of people (e.g., headaches, flushing), though scientific evidence of widespread sensitivity is limited.