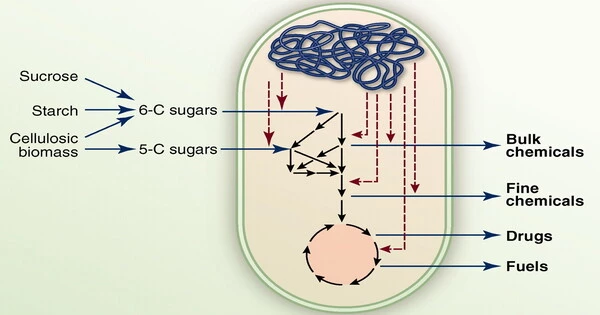
Metabolic engineering is a field of biotechnology that involves the manipulation of metabolic pathways in living organisms in order to improve or optimize the production of desirable compounds or to increase the efficiency of metabolic processes. This can be achieved through genetic manipulation, such as introducing new genes or modifying existing ones, as well as through environmental or biochemical manipulation of the organism’s growth conditions. Applications of metabolic engineering include the production of biofuels, pharmaceuticals, and industrial chemicals.
The goal of metabolic engineering is to improve the production of useful compounds such as drugs, biofuels, and chemicals, or to improve the organism’s ability to degrade pollutants or resist disease. It involves the use of techniques from genetics, biochemistry, and systems biology to understand and manipulate metabolic pathways.
Metabolic engineering is the process of modifying the metabolic pathways of living organisms to produce desired products or to enhance their growth, stress tolerance, or other properties. This is typically done by introducing or deleting genes, or by manipulating the expression levels of existing genes. It can be applied to a wide range of organisms, including bacteria, yeasts, algae, and plants, and is used in industries such as biofuels, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture.
It is the manipulation of an organism’s metabolic pathways to optimize or change the production of desired compounds or to improve its overall growth and performance. It is a multidisciplinary field that combines the principles of genetics, biochemistry, and systems biology to design and construct organisms with improved metabolic capabilities. Applications of metabolic engineering include the production of biofuels, pharmaceuticals, and industrial enzymes.
It is the manipulation of an organism’s metabolic pathways to improve or change the production of a specific chemical or compound. This can be done through genetic manipulation, selective breeding, or other techniques. The goal of metabolic engineering is to optimize the production of a desired product, such as biofuels, chemicals, or medicines, while minimizing waste and negative environmental impacts.
The ultimate goal of metabolic engineering is to be able to use these organisms to produce valuable substances on an industrial scale in a cost-effective manner. Current examples include the manufacture of beer, wine, cheese, pharmaceuticals, and other biotechnology products. Some common metabolic engineering strategies include (1) overexpression of the gene encoding the rate-limiting enzyme of the biosynthetic pathway, (2) blocking competing metabolic pathways, (3) heterologous gene expression, and (4) enzyme engineering.