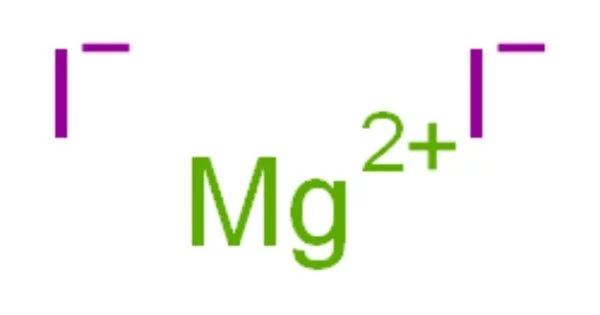Magnesium iodide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula MgI2. It is a white, odorless, crystalline solid, and is highly soluble in water. It is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula MgI2. MgI2•xH2O hydrates are formed. It is a magnesium and hydrogen iodide salt. These salts are highly soluble in water and are typical ionic halides.
Magnesium iodide can be prepared by reacting magnesium metal with iodine or by reacting magnesium oxide or magnesium hydroxide with hydroiodic acid.
Properties:
- It appears as a white crystalline solid.
- It has a molecular weight of 278.113 g/mol.
- It has a melting point of 637°C and a boiling point of 1,130°C.
- It is highly soluble in water and soluble in ethanol, acetone, and ether.
- It has a density of 4.43 g/cm³.
Preparation
Magnesium iodide can be prepared from magnesium oxide, magnesium hydroxide, and magnesium carbonate by treatment with hydroiodic acid:
MgO + 2 HI → MgI2 + H2O
Mg(OH)2 + 2 HI → MgI2 + 2 H2O
MgCO3 + 2 HI → MgI2 + CO2 + H2O
Reactions
Magnesium iodide is stable at high temperatures in a hydrogen atmosphere, but decomposes in air at normal temperatures, turning brown due to elemental iodine release. When heated in air, it completely decomposes to magnesium oxide.
Another way to make MgI2 is to combine powdered elemental iodine and magnesium metal. To obtain anhydrous MgI2, the reaction should be carried out in a strictly anhydrous atmosphere, with dry-diethyl ether as a solvent. When magnesium iodide is used in the Baylis-Hillman reaction, it produces (Z)-vinyl compounds.
Uses
Magnesium iodide has few commercial uses, but can be used to prepare compounds for organic synthesis. It is commonly used as a catalyst in organic synthesis reactions, such as the Grignard reaction. It can also be used as a source of iodine in chemical reactions or as a dehydrating agent. Additionally, magnesium iodide is used in the production of magnesium metal and as a component in antifreeze solutions.
Hazards
Magnesium iodide is not considered toxic, but it can cause irritation to the eyes, skin, and respiratory system. It can react violently with strong oxidizing agents, acids, and bases.
Like other magnesium compounds, magnesium iodide can be toxic if ingested or inhaled, and can cause skin and eye irritation upon contact. It is important to handle magnesium iodide with care and to follow proper safety precautions when working with this compound.