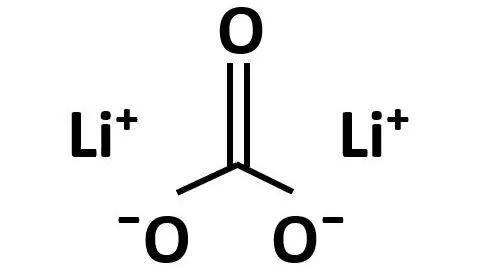
Lithium carbonate is an inorganic compound that is the lithium salt of carbonate with the formula Li2CO3. It is the carbonate salt of lithium, a soft alkali metal with antimanic and hematopoietic properties. This white salt is widely used in the processing of metal oxides. It is on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines because it can be used to treat mood disorders such as bipolar disorder.
Lithium carbonate appears as a white powder. When dissolved in water, it produces a strong irritant. It is both a lithium salt and a carbonate salt. It functions as an antimanic medication. It is widely used in the processing of metal oxides and has received attention for its use in psychiatry. It is an important industrial chemical.
Properties
Lithium carbonate is a white powder with no odor. It has a density of 2.11 g mL-1. The melting point of lithium carbonate is 724 degrees Celsius, and its boiling point is 1310 degrees Celsius. Hot water, acetone, ammonia, and ethanol are all insoluble. It is insoluble in cold water (its solubility in water decrease with the increasing temperature). Acetic acid dissolves it.
- Chemical formula: Li2CO3
- Molar mass: 73.89 g/mol
- Appearance: Odorless white powder
- Density: 2.11 g/cm3
- Melting point: 723 °C (1,333 °F; 996 K)
- Boiling point: 1,310 °C (2,390 °F; 1,580 K);
- Decomposes from ~1300 °C
- Solubility in water: 1.54 g/100 mL (0 °C); 0.69 g/100 mL (100 °C)
- Solubility product (Ksp): 8.15×10−4
- Solubility: Insoluble in acetone, ammonia, alcohol

Reactions
Unlike sodium carbonate, which has at least three hydrates, lithium carbonate only exists as an anhydrous compound. In comparison to other lithium salts, it has a low water solubility. The extraction of lithium from aqueous extracts of lithium ores takes advantage of this low solubility. Its apparent solubility increases 10-fold under mild carbon dioxide pressure; this effect is due to the formation of the more soluble metastable bicarbonate:
Li2CO3 + CO2 + H2O ⇌ 2 LiHCO3
The extraction of lithium carbonate at high pressures of CO2 and its precipitation upon depressurizing is the basis of the Quebec process.
Lithium carbonate can also be purified by exploiting its diminished solubility in hot water. Thus, heating a saturated aqueous solution causes crystallization of Li2CO3.
Lithium carbonate, and other carbonates of group 1, do not decarboxylate readily. Li2CO3 decomposes at temperatures around 1300 °C.
Production
Lithium is primarily extracted from two sources: spodumene from pegmatite deposits and lithium salts from underground brine pools. In 2020, approximately 82,000 tons were produced, indicating significant and consistent growth.
Uses
The industrial chemical lithium carbonate is very important. Its primary application is as a precursor to compounds used in lithium-ion batteries. It is primarily used in the pharmaceutical industry to treat manic-depressive psychosis. It is also used in the chemical industry to make other lithium compounds, particularly lithium salts such as lithium chloride and lithium bromide.
- Rechargeable batteries
Lithium carbonate (and lithium hydroxide) are primarily used as a precursor to lithium compounds used in lithium-ion batteries. In practice, lithium compounds are used to make two components of the battery: the cathode and the electrolyte.
The electrolyte is a lithium hexafluorophosphate solution, and the cathode is one of several lithiated structures, the most common of which are lithium cobalt oxide and lithium iron phosphate. Before converting to the compounds listed above, lithium carbonate can be converted into lithium hydroxide.
- Medical uses
Lithium carbonate was first used to treat bladder stones in 1843. Some doctors recommended lithium salt therapy in 1859 for a variety of ailments, including gout, urinary calculi, rheumatism, mania, depression, and headache. John Cade discovered the anti-manic effects of lithium ions in 1948. This discovery led to the use of lithium, specifically lithium carbonate, to treat manias associated with bipolar disorder.
Health effects
Ingestion of large amounts of lithium carbonate can be extremely toxic. It can also cause side effects and diseases like nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. It does not burn.