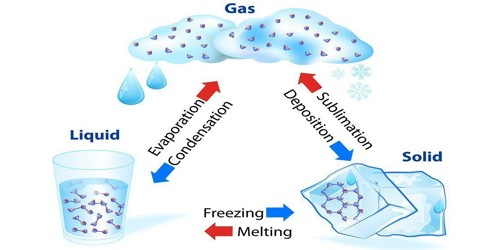
A liquid is a form of matter. It is settled between solid and gas. It has a defined volume but can change state. An example is a liquid water. Liquid has an almost-fixed volume, but no set shape. It is a sample of matter that conforms to the shape of a container in which it is held, and which acquires. Common Examples: Water, Milk, Blood, Urine, Gasoline, etc. Mercury is the only metallic element that is a liquid at room temperature, although francium, cesium, gallium, and rubidium liquefy at slightly elevated temperatures.
Every small force makes a liquid change its shape by flowing. Because of that, gravity makes liquids always take the shape of the container. The molecules that make up the liquid can freely move among themselves. Liquids consist of atoms or molecules that are connected by intermolecular bonds. The particles in liquids are not as closely bonded, arranged and fixed in place as in solids.
The density of a liquid is usually close to that of a solid, and much higher than in a gas. Fluids that flow slowly have a high viscosity. Some fluids like tar have such a high viscosity that they may seem solid.
It is difficult to compress a liquid. Much like solids, liquids (most of which have a lower density than solids) are incredibly difficult to compress. If a liquid is cooled down until it is colder than a certain temperature, it will become a solid. This temperature is called the melting point or freezing point and is different for every different type of liquid. If a liquid is heated up it becomes a gas. This process of a liquid changing to a gas is called evaporation. The temperature this happens at is called the boiling point. When a solid is heated above its melting point, it becomes liquid because the pressure is higher than the triple point of the substance.
In a liquid, the liquid on the top presses down on the liquid underneath, so at the bottom, the pressure, p, is bigger than at the top. The equation for working this out is- p = ρgz.
where z is the depth of the point below the surface and g is how strong gravity is pulling on the liquid. ρ is a number that tells us how heavy a set amount of the liquid is. We call this the density and it is different for all liquids.