Lanthanum stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of lanthanum and stearic acid with the chemical formula La(C18H35O2)3. It is a chemical compound formed from lanthanum and stearic acid. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
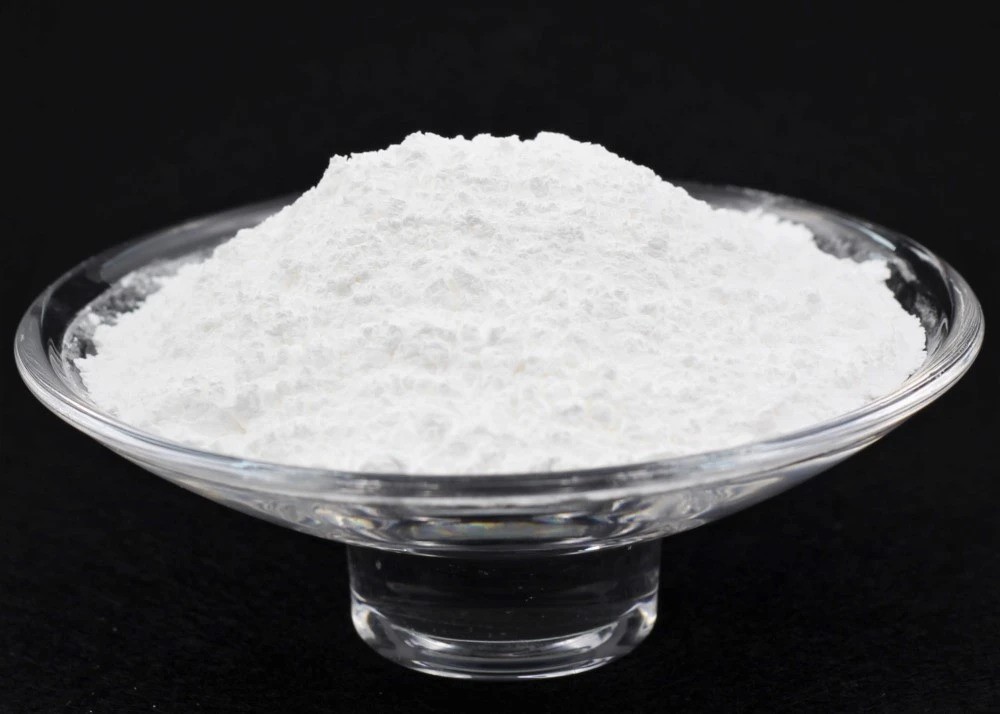
The compound forms a white powder that is soluble in benzene. It can enhance the thermal stability and lubricity of polymers. It serves as a catalyst in certain chemical reactions.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C54H105LaO6
- Molar mass: 989.3
- Appearance: white powder
- Solubility in water: insoluble
- Melting Point: Varies, but generally above 200 °C, depending on the specific form and purity.
- Density: Around 0.9 to 1.1 g/cm³.
- Stability: Relatively stable under standard conditions, but may degrade under extreme conditions or when exposed to strong acids.
Occurrences
- Natural Occurrence: Lanthanum is not found in its elemental form in nature but is found in minerals like monazite and bastnäsite, which are sources of rare earth elements. Stearic acid, on the other hand, is commonly found in animal and vegetable fats.
- Synthesis: It can be synthesized through the reaction of lanthanum salts with stearic acid. It’s often produced in laboratory settings or industrial applications.
Uses
Lanthanum stearate is mainly used as a nucleating agent for plastics degradation and heat stabilizer for PVC.
- Lubricants: Used as a lubricant additive in some applications due to its properties.
- Ceramics: Employed in the production of certain ceramics and composites.
- Catalysts: Can act as a catalyst or catalyst support in chemical reactions.