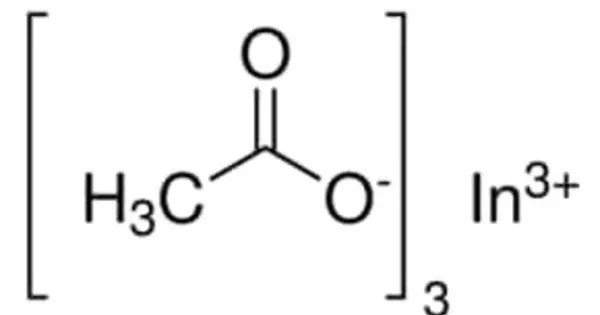
Indium acetate is an acetate of indium, with the chemical formula In(CH3COO)3. It is soluble in water, acetic acid and mineral acids. It is the precursor of indium-containing compounds such as the solar cell materials CuInS2 and indium phosphide quantum dots. It can act as a Lewis acid due to the indium ion and may react with various nucleophiles, especially those containing oxygen or nitrogen atoms.
Properties
It typically appears as a white to colorless crystalline solid. It is soluble in water and organic solvents, such as ethanol. It is reactive with strong bases, acids, and certain reducing agents, releasing indium compounds in these reactions.
- Chemical formula: In(CH3COO)3
- Molar mass: 291.96
- Appearance: white hygroscopic powder
- Solubility: It is soluble in water and other polar solvents like ethanol, acetone, and methanol.
- Stability: Indium acetate is generally stable, but it should be stored in a dry environment to prevent decomposition, especially in the presence of moisture.
- Melting Point: It decomposes rather than melting at high temperatures.
Preparation
Indium acetate can be prepared by reacting indium or triethylindium with frozen acetic acid.
Indium acetate can be prepared by reacting indium metal or indium oxide (In₂O₃) with acetic acid (CH₃COOH), producing indium acetate and water. Here’s a general reaction:
In2O3 + 6 CH₃COOH → 2In(C₂H₃O₂)₃ + 3H₂OIn2O3 +3H₂O
Chemical properties
Indium acetate can react with propionic acid:
In(CH3COO)3 + CH3CH2COOH → In(CH3COO)2(CH3CH2COO) + CH3COOH
Occurrence
Naturally, indium does not occur in large quantities in the Earth’s crust, and it is mostly obtained as a by-product from zinc, lead, and copper mining. Indium is rare and typically recovered from ores such as sphalerite (zinc ore), which contains trace amounts of indium.
Uses
- Catalysis: Indium acetate is used as a catalyst in various chemical reactions, especially in the production of organic compounds.
- Electronics: It is sometimes used in the synthesis of thin films or materials for electronic devices, such as semiconductors.
- Precursor for indium compounds: Indium acetate can be a precursor for the preparation of other indium-based compounds.
Safety
Indium acetate is generally considered to be of low toxicity, but as with all chemicals, it should be handled with care. Proper safety measures like gloves, goggles, and working in a well-ventilated area should be taken.