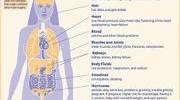
A high fat diet is a dietary approach that emphasizes the consumption of foods that are high in fat, often at the expense of other macronutrients like carbohydrates and protein. Typically, a high fat diet is defined as one that derives 60% or more of its calories from fat.
There are several types of high fat diets, including the ketogenic diet, which is a very low carbohydrate, high fat diet that is designed to promote the production of ketones by the liver as a source of energy. Other high fat diets include the Atkins diet, which is also low in carbohydrates but allows for more protein, and the Mediterranean diet, which is high in healthy fats like olive oil and nuts.
For decades, variations of the high-fat diet have been popular. The Atkins Low Carb Diet and various variations on the ketogenic diet are two examples. Although there are vegan ketogenic diets, cyclical ketogenic diets, a diet that combines elements of the Mediterranean and ketogenic diets, and many more variations with varying degrees of strictness, these diets are generally very high in fat, high in protein, and low in carbohydrate. The preferred label, low-carb diet, may have a marketing rationale, but we might as well call them high-fat diets because, in order to reduce carbohydrate intake to the level considered “healthy” by these diets, the proportion of fat in the diet must by necessity be high.
While high fat diets have been controversial in the past, recent research suggests that they may have some health benefits, such as improving insulin sensitivity, reducing inflammation, and promoting weight loss. However, it’s important to note that not all fats are created equal, and a high fat diet can also be high in unhealthy saturated and trans fats, which can increase the risk of heart disease and other health problems. As with any dietary approach, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting a high fat diet.
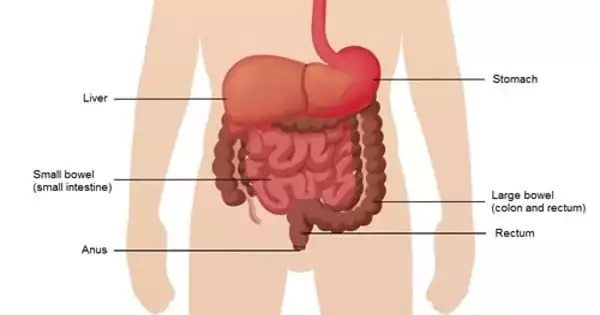
A high-carbohydrate diet causes your body to get its energy from glucose, which comes from carbohydrates. When you consume a lot of carbohydrates, your body produces more glucose than it can use. The extra glucose is then stored as fat. In contrast, a high-fat diet causes your body to use ketones from the fat you eat for energy. However, the process of obtaining these ketones from fat consumes a significant amount of energy. So, in essence, your body is working to obtain energy, which consumes a lot of energy and may result in weight loss.
Furthermore, a high-fat diet quickly gives you a feeling of fullness, with many people eating less than they would with a high-carbohydrate diet. In many cases, this type of diet may be beneficial to those suffering from heart disease, certain types of cancer, type 2 diabetes, and even Alzheimer’s disease.
It’s worth noting that a high-fat diet can mean different things to different people and may have different effects depending on individual factors such as genetics, activity level, and overall health status. Therefore, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet.