The Green Economy is an economic model that prioritizes sustainable development and environmental protection. It seeks to balance economic growth with environmental sustainability by encouraging the use of renewable energy sources, reducing waste and pollution, and promoting resource efficiency. The Green Economy encompasses various industries, such as renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, green transportation, and waste management.
The Green Economy aims to create new job opportunities while promoting sustainable economic growth. It can also help mitigate climate change, reduce biodiversity loss, and promote social equity. The concept of the Green Economy has gained significant attention in recent years, as countries around the world seek to transition to a more sustainable future. Many governments, businesses, and civil society organizations have adopted policies and initiatives to promote the Green Economy, such as renewable energy targets, carbon pricing, and green procurement.
A green economy is one that seeks to reduce environmental risks and ecological scarcity while also pursuing sustainable development without degrading the environment. It is related to ecological economics but has a more political application. According to the UNEP Green Economy Report 2011, “that in order to be green, an economy must be both efficient and fair. Fairness entails recognizing global and national equity dimensions, particularly in ensuring a Just Transition to a low-carbon, resource-efficient, and socially inclusive economy.”
The transition to a green economy requires significant investments in clean technologies, sustainable infrastructure, and education and training programs. Governments, businesses, and individuals all have a role to play in supporting this transition, by adopting sustainable practices, investing in green technologies, and advocating for policies that promote environmental protection and sustainability.
The direct valuation of natural capital and ecological services as having economic value distinguishes it from previous economic regimes, as does a full cost accounting regime in which costs externalized onto society via ecosystems are reliably traced back to, and accounted for as liabilities of, the entity that causes the harm or neglects an asset.
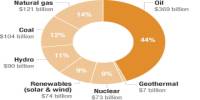
The green economy encompasses a wide range of sectors and industries, including renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, green transportation, eco-tourism, and waste management. It also includes the development of new green jobs, such as renewable energy technicians, green architects, and environmental consultants. Overall, the Green Economy is a promising approach to achieving sustainable development and addressing the pressing environmental challenges facing the world today.