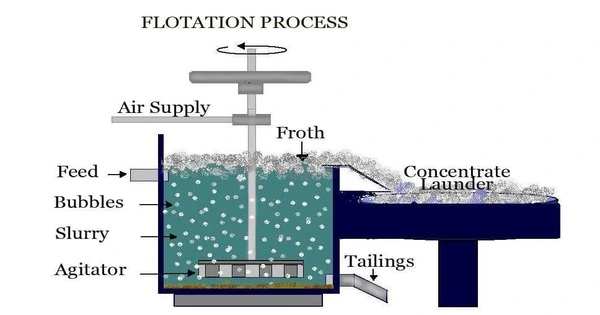
Froth flotation is a method for separating hydrophobic from hydrophilic materials. It is a popular separation method in mineral processing for selectively separating hydrophobic minerals from hydrophilic ones. This is employed in the mineral processing, paper recycling, and wastewater treatment sectors. It is a method that uses differences in particle surface characteristics to produce separation.
Historically, this was originally utilized in the mining industry, where it was one of the most important enabling technologies of the twentieth century. It has been described as “the single most important operation used for the recovery and upgrading of sulfide ores”.
The discovery of froth flotation has enhanced the recovery of precious minerals, including copper and lead. Along with mechanical mining, it has enabled the profitable recovery of important metals from considerably lower-grade ore than before.
The process involves several key steps:
- Grinding: The ore is crushed and ground into fine particles to increase the surface area for interaction with chemicals.
- Conditioning: The ground ore is mixed with water and various chemicals, such as collectors and frothers. Collectors are chemicals that selectively bind to the surface of the target mineral, making it hydrophobic (water-repellent). Frothers, on the other hand, create a stable froth at the surface of the flotation cell.
- Air Injection: Air is introduced into the mixture, creating bubbles. The hydrophobic particles attach to the bubbles and float to the surface, forming a froth layer.
- Skimming: The froth containing the hydrophobic particles is skimmed off from the top of the flotation cell.
- Deinking (optional): In some cases, a deinking step may be included to remove unwanted materials from the froth.
Applications
Froth flotation is commonly employed in the mining sector to concentrate a variety of minerals, including sulfide minerals (copper, lead, zinc), oxide minerals (hematite, magnetite), and industrial minerals (potash, phosphate). The method is also employed in environmental applications including water purification and recycling.
The success of froth flotation is dependent on careful control of several parameters, including the type and concentration of reagents, pH, particle size, and the design of the flotation equipment. Researchers and engineers are constantly working to improve the efficiency and selectivity of the process for various ore types and operating conditions.