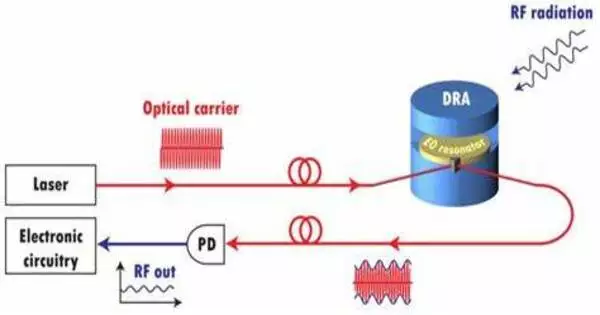
A dielectric wireless receiver is a device that captures wireless signals by using dielectric materials, which are insulators that do not carry electricity. It is a radiofrequency receiver front-end with no electronic circuitry or metal interconnects. These materials are used to improve the reception and transmission of electromagnetic waves in wireless communication systems.
Dielectric materials, like as ceramics or plastics, are utilized in antennas and other components to increase signal quality and performance. It provides protection against damage caused by powerful electromagnetic radiation emitted by EMP and HPM sources. This receiver is known as ADNERF (an acronym for All-Dielectric Non-Electronic Radio Front-End). ADNERF is a form of Electro-Magnetic Pulse Tolerant Microwave Receiver (EMPiRe).
Background
The ongoing trend toward smaller feature size and voltage in integrated circuits makes modern devices extremely vulnerable to harm from High Power Microwave (HPM) and other microwave-based directed energy sources. These cause high voltage transient surges of hundreds of volts, which can punch through the gate insulator in the transistor and ruin the circuit’s metal interconnects. To protect electronic systems from such attacks, the “soft spots” (metal and transistor) in a traditional receiver front-end must be avoided.
Dielectric materials can be used in various ways in wireless receivers, including:
- Antennas: Dielectric materials can be included into antenna designs to improve their performance. For example, dielectric resonator antennas (DRAs) use dielectric materials to improve antenna efficiency and radiation pattern.
- Waveguides: Dielectric waveguides can be used to route and alter electromagnetic waves, notably in the millimeter-wave and terahertz frequency ranges. Dielectric waveguides are non-metallic and have low loss, making them appropriate for high-frequency applications.
- Lens Antennas: Dielectric lens antennas focus electromagnetic waves in the same way that optical lenses do. These antennas are utilized in applications requiring high gain and directivity.
- Matching Networks: Dielectric materials can be employed in impedance matching networks to ensure that the antenna’s input impedance matches the receiver’s output impedance, increasing power transfer.
Application
Dielectric wireless receivers are widely employed in wireless communication systems such as mobile phones, satellite communication, radar systems, and others. In these systems, the use of dielectric materials improves signal reception and transmission, reduces interference, and improves overall system performance.