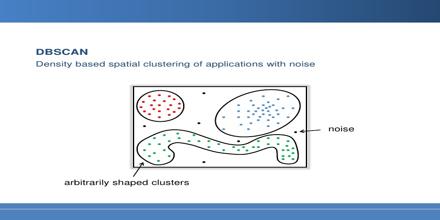
Density Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN) can identify clusters in large spatial data sets by looking at the local density of database elements, using only one input parameter. DBSCAN can also determine what information should be classified as noise or outliers. In spite of this, its working process is quick and scales very well with the size of the database almost linearly. DBSCAN can find arbitrarily shaped clusters. It can even find a cluster completely surrounded by a different cluster. Due to the MinPts parameter, the so-called single-link effect is reduced.
Density Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN)