Analysis of credit management of Janata Bank Limited
Janata means people. This is a progressive Bank. Immediately after the emergence of Bangladesh in 1971, the erstwhile United Bank Limited and Union Bank Limited were nationalized and renamed as Janata Bank. It has been operating since it’s inception in 1972 both in Bangladesh and overseas. Janata Bank Ltd. has been playing a significant role in the economic development of the country by mobilizing savings and distributing funds into different productive sectors. It is also a major player in the fields of micro-credit and software development.
Janata Bank has an authorized capital of Tk. 20000 million (approx. US$ 250 million), paid up capital of Tk. 19140.00 million, reserve of Tk.17976.20 million. The Bank has a total asset of Tk. 586082.98 million as on 31st December 2013. Immediately after the emergence of Bangladesh in 1971, the erstwhile United Bank Limited and Union Bank Limited were renamed as Janata Bank. On 15th November, 2007 the bank has been corporatised and renamed as Janata Bank Limited.
- Janata Bank Limited operates through 898 branches including 4 overseas branches at United Arab Emirates. It is linked with 1239 foreign correspondents all over the world.
- The Bank employees more than 15(fifteen) thousand persons.
- The mission of the bank is to actively participate in the socio- economic development of the nation by operating a commercially sound banking organization, providing credit to viable borrowers, efficiently delivered and competitively priced, simultaneously protecting depositors funds and providing a satisfactory return on equity to the owners.
- The Board of Directors is composed of 13 (Thirteen) members headed by a Chairman. The Directors are representatives from both public and private sectors.
- The Bank is headed by the Chief Executive Officer & Managing Director, who is a reputed banker.
- The corporate head office is located at Dhaka with 10 (ten) Divisions comprizing of 44 Departments.
CREDIT PROGRAM
General and Industrial Credit:
Janata Bank Ltd. has formulated its policy to give priority to small and medium business while financing large scale enterprise through consortium of banks total loan and advance of the bank stood at BDT 478,535 million as of December 31, 2013 as compared to BDT 409,767 million in 2012. Increase rate is 16.78% compared to 2012. Following the guideline of Bangladesh Bank, credit facilities have been extended to productive and priority sectors. In extending credit facilities, the Bank has given due importance to the needs and requirements of both public and private sectors. Major sectors include Jute, Textile Ind. & trade, Steel & Engineering, Food & Allied, and Export & Import etc.
LOANS AND ADVANCES:
The main focus of Janata Bank Ltd. Credit Line/Program is financing business, trade and industrial activities through an effective delivery system. Janata Bank Ltd. offers credit to almost all sectors of commercial activities having productive purpose. The loan portfolio of the Bank encompasses a wide range of credit programs covering about 200 items. Credit is also offered to 15 (fifteen) thrust sectors, as earmarked by the govt., at a reduced interest rate to develop frontier industries. Credit facilities are offered to individuals, businessmen, small and big business houses, traders, manufactures, corporate bodies, etc.
Following the guidelines of Bangladesh Bank, credit facilities have been extended to productive and priority sectors. The outstanding advance of the bank is Tk.478,535 million on 31st December 2013.In credit facilities, the Bank has given due importance to the needs and requirements of both public and private sector.
OBJECTIVES OF THE REPORT
The objectives of the report are to determine how credit policy applied in sanctioning and recovering loans and advances. Credit policy varies in terms of loan sector, status of the organization, government policy, fiscal budget and guidelines etc.
Specific objectives:
- To present an overview of Janata Bank Limited(JBL)
- To assess the credit structure of the JBL in practice.
- To measure the effectiveness of the bank in the utilization of available resources.
- To identify the recovery performance of JBL.
- To point out the problems in fund utilization and recovery thereon.
- To make a critical reasoning in respect to the treatment of provision for bad and doubtful credit.
- To assess and highlight on the legal actions followed by the JBL.
- To find out the extent of similarities and dissimilarities in the course of action followed by Janata Bank. Limited.
- To compare the credit supervision of. JBL
- To compare the quantitative change from phase-1 (1998-2002) to phase-2 (2003- 2010).
- To find out problems and suggesting recommendations for further improvement.
Credit Management
Loans or credits comprise the most important asset as well as the primary source of earning for the banking institutions. On the other hand, loan/credit is also the major source of risk for the bank management. A prudent bank management should always try to make an appropriate balance between its return and risk involved with the loan portfolio. Credit appraisal process is the tool, which helps the bank to predict the risk and return on the proposed project for credit disbursement. To get a clear idea about credit appraisal process we need to know the key factors of credit appraisal procedures.
Credit:
The word credit is derived from the Latin word “credo” which means “I believe” and is usually defined as the ability to buy with a promise to pay. It consists of actual transfer and delivery of goods and services in exchange for a promise to pay in future. It is simply the opposite of debt.
Diversification of banking service has accelerated the use of credit in the expansion of business operation. It is a fundamental precept of banking everywhere that advances are made to customers in reliance on his promise to pay rather than the security held by the banker.
Principles of Credit: A prudent Banker should always adhere to the following general principles of lending funds to his customers.
- Background, Character and ability of the borrowers
- Purpose of the facility,
- Term of facility,
- Safety,
- Security,
- Profitability,
- Source of repayment
PROCESS OF CREDIT MANAGEMENT
Credit management must be organized in such a process that the bank can minimize its losses for payment of expected dividend to the shareholders. The purpose of this process is to provide directional guidelines that will improve the risk management culture, establish minimum standards for segregation of duties and responsibilities, and assist in the ongoing improvement of concerned bank.
The guidelines for credit management may be organized into the following sections:
Policy guidelines:
- Lending guidelines
- Credit assessment and risk grading
- Approval authority
- Segregation of duties
- Internal control and compliance
Management structure and responsibilities
Program guidelines:
- Approval process
- Credit administration
- Credit monitoring
- Credit recovery
Program guidelines
- Approval process: The following diagram illustrates an example of the approval process:
- Credit administration: The credit administration function is critical in ensuring that proper documentation and approvals are in place prior to the disbursement of loan facilities.
- Credit monitoring: To minimize credit losses, monitoring procedures and systems should be in place that provides an early indication of the deteriorating financial health of borrower.
- Credit recovery: The recovery unit of branch should directly manage accounts with sustained deterioration (a risk rating of sub-standard or worse). The primary functions of recovery unit are:
- Determine account action plan/ recovery strategy
- Pursue all options to maximize recovery, including placing customers into receivership or liquidation as appropriate.
- Ensure adequate and timely loan loss provisions are made based on actual and expected losses.
TOOLS OF CREDIT MANAGEMENT
For credit management, a firm may use tools available to them. Such tools include Credit Risk Grading (CRG) and Financial Spread Sheet (FSS). Credit risk grading is an important for credit risk management as it helps the banks and financial institutions to understand various dimensions of risk involved in different credit transactions. The aggregation of such grading across the borrowers, activities and the lines of business can provide better assessment of the quality of credit portfolio of a bank or branch.
The Lending Risk Analysis (LRA) manual introduced in 1993 by the Bangladesh Bank has been in practice for mandatory use by the banks and financial institutions for loan size of BDT 1.00 crore and above. However, the LRA manual suffers from a lot of subjectivity, sometimes creating confusion to the lending bankers in terms of selection of credit proposals on the basis of risk exposure. Meanwhile in 2003 end, Bangladesh Bank provided guidelines for credit risk management of banks wherein, it recommended for the introduction of Risk Grade Score Card for risk assessment of credit proposals.
Bangladesh Bank expects all commercial banks to have a well defined credit risk management system which delivers accurate and timely grading. In practice, a bank’s credit risk grading system should reflect the complexity of its lending activities and the overall level of risk involved.
Definition of Credit Risk Grading (CRG)
- The Credit Risk Grading (CRG) is a collective definition based on the pre- specified scale and reflects the underlying credit-risk for a given exposure.
- A Credit Risk Grading deploys a number/ alphabet/ symbol as a primary summary indicator of risks associated with a credit exposure.
- Credit Risk Grading is the basic module for developing a Credit Risk Management system.
Functions of Credit Risk Grading
Well-managed credit risk grading systems promote bank safety and soundness by facilitating informed decision-making. Grading systems measure credit risk and differentiate individual credits and groups of credits by the risk they pose. This allows bank management and examiners to monitor changes and trends in risk levels. The process also allows bank management to manage risk to optimize returns.
Use of Credit Risk Grading
- The Credit Risk Grading matrix allows application of uniform standards to credits to ensure a common standardized approach to assess the quality of individual obligor, credit portfolio of a nit, line of business, the branch or the bank as a whole.
- As evident, the CRG outputs would be relevant for individual credit selection, wherein a borrower or a particular exposure/ facility are rated. The other decisions would be related to pricing (credit-spread) and specific features of credit facility. These would largely constitute obligor level analysis.
- Risk grading also be relevant for surveillance and monitoring, internal MIS and assessing the aggregate risk portfolio level analysis.
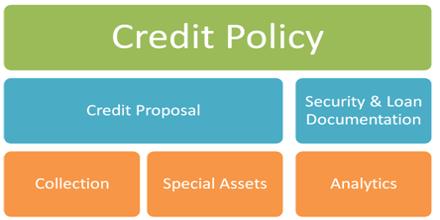
Credit Policy
MEANING OF CREDIT POLICY
Policy entails projected course of action. Janata Bank Ltd. has its own policy granting credit although credit is always a matter of judgment applying common sense in the light of one’s experience.
A sound credit policy includes among other things safety of funds invested vis-à-vis profitability of the bank. Encouraging maximum number of small loans is better than concentration in a particular type of advances, which ensures sufficient liquidity with least incidence of bad debts.
It has to be borne in mind that a good loan allowed to a properly selected borrower is half collected. In order to make a good loan there should have a good loan policy.
OBJECTIVE OF CREDIT POLICY
There are some objectives behind a written credit policy of Janata Bank Ltd. that are as follows;
- To provide a guideline for giving loan.
- Prompt response to the customer need.
- Shorten the procedure of giving loan.
- Reduce the volume of work from top level management.
- Delegation of authority of work from top level of management.
- To check and balance the operational activities
FORMULATION OF CREDIT POLICY
One of questions that should arise in a discussion of credit is who should formulate the policy. Although the ultimate responsibilities lay at the highest level in the organization i.e. the board of directors. Yet the actual drafting shall have to be done by the senior lending office in consultations with the chief executive officer and with contribution from senior officers, associates and subordinates. Obviously the level of origin will vary with the size and structure of the organization. The matter then referred to the board for approval after careful examination consideration and discussion.
ESSENTIAL COMPONENTS OF A SOUND CREDIT POLICY:
There can be some variations based on the needs of a particular organization, but at least the following areas should be covered in any comprehensive statement of credit policy and JBL’s policy also covers these areas:
- Legal consideration: The bank’s legal lending limit and other constraints should be set forth to avoid inadvertent violation of banking regulations.
- Delegation of authority: Each individual authorized to extend credit should know precisely how much and under what conditions he or she may commit the bank’s funds. These authorities should be approved, at least annually, by written resolution of the board of directors and kept current at all times.
- Types of credit extension: One of the most substances parts of a loan is a delineation of which types of loans are acceptable and which type are not.
- Pricing: In any profit motivated endeavor, the price to be charged for the goods or services rendered is of paramount without it, individuals have few guidelines for quoting retag or fees, and the variations resulting from human nature will be a source of customer dissatisfaction.
- Market Area: Each bank should establish its proper market area, based upon, among other things, the size and sophistication of its organization its capital standpoint, defining one’s market area is probably more important in the lending function than in any other aspect of banking.
- Loan Standard: This is a definition of the types of credit to be expended, wherein the qualitative standards for acceptable loans are set forth.
- Credit Granting procedures: This subject may be covered in separate manual, and usually is in larger banks. At any rate, it should not be overlooked because proper procedures are essential in loan establishing policy and standards.
Without proper procedure for granting credit and constant policing to ensure that these procedures are meticulous carried out, the best conceived loan policy will not function and inevitable, problems will develop.
LENDING GUIDELINES:
As the bank have a high rate of non-performing loans. Banks risk taking applied should be contained and our focus should be to maintain a credit portfolio keeping in mind of bank’s capital adequacy and recovery strength. Thus bank’s strategy will be invigorating loan processing steps including identifying , measuring , containing risks as well as maintaining a balance portfolio through minimizing loan concentration , encouraging loan diversification , expanding product range , streamlining security , insurance etc. as buffer again unexpected cash flow .
Industry and business segment focus
Industry segment focuses on Textile, Pharmaceuticals, Agro-based, Food and allied, Telecommunication, Power generation and distribution, Health care, Entertainment Services, Chemicals, Transport, Infrastructure development, Linkage industry, Information technology, Ceramics, Others as decided from tome to time. And business segment focuses on Distribution, Brick field, Rice mill/ flour mill/ oil mill, Work order, Yarn trading, Cloth merchant, Industrial spares, Hardware, Electronic and electrical goods, Construction materials, Fish trading, Grocery, Wholesale/ retail, Others as dedicated from time to time
Types of credit facilities: Bank will go for
- Term financing for new project had BMRE of existing projects (large, medium, SME, SCI).
- Working capital for industries, trading services and others (large , medium, SME, SCI).
- Trade finance for import and export
- Lease finance
- Small loan for traders, micro enterprise and other productive small venture.
- Consumer finance
- Fee business
Fund Investment by Janata Bank
The principal function of a bank is to lend. Lending is a dynamic activity. It is through the medium of lending the banking industry promotes economic activity, instills and encourages, at the individual level, the principal of self-reliance, and yield earnings for the bank. It is lending alone that brings banking into a more meaningful and purposeful contract with public and, therefore, has the greatest impact upon them.
Proper utilization of fund is an essential pre-requisite of successful bank management. The procurements of funds supported by an efficient deployment of that procured fund lead a bank to the highest point of profitability. I would try to concentrate on Janata Bank Ltd.’s nature, pattern, and allocation of invested resources in this chapter. The bank under study has divergence in its investment portfolio, loan programs, advances and recovery rate etc.
ECONOMIC SECTOR WISE DISTRIBUTION OF FUND
Janata Bank Ltd. is engaged in extending long, medium and short term loans to various economic sectors in the country. As Janata Bank Ltd. extends its credit programs all over the economy such as agricultural credit program, industrial credit program and commercial financing, the bank tries to achieve significant profit from its operations and also to improve the economic conditions of the general public of the country.
Procedure of Loan Disbursement of Janata Bank Ltd.
Janata Bank Ltd. collects credit information about the applicant to determine the credit worthiness of the borrower. The bank collects the information about the borrower from the following sources:
- Personal investigation.
- Confidential report from other bank Head Office/Branch/chamber of the commerce.
- CIB Report from Central Bank.
INFORMATION COLLECTION
The loans and advances department gets a form filled by the party seeking a lot of information.
The information is listed below:
- Name and address of the borrower (present and permanent).
- Constitution or status of the business.
- Data of establishment and place of incorporation.
- Particulars of properties, partners and Directors.
- Background and business experience of the borrowers.
- Particulars of personal assets, name of subsidiaries, percentage of share holding and nature of business.
- Details of liabilities in name of borrowers, in the name of any directors.
- Financial Statement of the last three years.
- Nature and details of business/products.
- Details of securities offered.
- Proposed debt equity ratio.
- Other relevant information.
ANALYZING THESE INFORMATION
Janata Bank Ltd. then starts examination whether the loan applied for, is complying with its lending policy. If comply, then it examines the documents submitted and the credit worthiness. Credit worthiness analysis, i.e. analysis financial conditions of the loan applicant is very important. If loan amount is more than 50, 00,000, then bank goes for Lending Risk Analysis (LRA) and Spreadsheet Analysis (SA) which are recently introduced by Bangladesh Bank.
According to Bangladesh Bank Rules, LRA and SA are a must for the loan exceed of one crore. If these two analyses reflect favorable condition and document submitted for the loan appeared to be satisfactory, then bank goes for further action.
LENDING RISK ANALYSIS (LRA)
LRA is a very important and vital analysis for deciding whether the loan proposal is potential or not. Many types of scientific, mathematical, statistical and managerial tools and devices are required to perform this analysis. Janata Bank Ltd. maintains a prescribed format for Lending Risk Analysis, which includes a spreadsheet to analyze a lot of things. It is not possible to discuss the entire LRA in this report.
Lending Risk Analysis (LRA)
Industry Risk:
- Supply Risk- What is the risk of failure to disruption in the supply of input?
- Sales Risk- What is the risk of failure due to disruption sales?
- Company Risk:
- Company Position Risk:
- Performance Risk- What is the risk if the company position is so weak that it can not perform well enough to repay the loan, given expected external condition?
- Resilience Risk- What is the risk of failure due to lack of resilience to unexpected external condition?
Management Risk:
- Management Competence Risk- What is the risk of failure due to lack of management competence?
- Management Integrity Risk- What is the risk of failure due to lack of Management Integrity?
Security Risk:
- Security Control Risk- What is the risk that the bank fail to realize the security?
- Security Cover Risk- What is the risk that realized security value is less than the exposure?
PROPOSAL ANALYSIS
The Project Proposal is analyzed and decision about the project is taken. The loans and advance department is responsible for the analysis. After preliminary appraisal of the loan project the final approval is obtain from the manager. If the loan amount crosses a certain amount (no found), managers send the loan project to the principal office for final approval. The experts in principal office find out different projected ratios and developed and understanding about the potentiality of the project. Bank evaluates a loan proposal by considering few predetermined variables. These are:
- Safety
- Liquidity
- Profitability
- Security
- Purpose of the loans
- Sources of repayment
- Diversification of risk etc.
The most important measure of appraising a loan proposal is safety of proposal. Safety is measured by the security offered by the borrower and repaying capacity of the borrower. The attitude of the borrower is also important consideration. Liquidity means the inflow of cash into the project in course of its operation. The profit is the blood of any commercial institution.
Before approval of any loan project the bank authority has to ensure that the proposed project will be profitable venture. Profitability is assessed from the projected Profit and Loss Statement. The security is the only tangible asset remains with the banker. Securing of collateral is the only weapon to recover the loan amount. So bank has to see that the collateral is easy to sale and sufficient to recover the loan amount. Bank can not sanction loan by only depending on collateral.
The sources of the payment of the project should be a feasible one. During sanctioning any loan Bank has to be attentive about diversification of risk. All money must not be disbursed amongst a small number of people. In addition any project must be established for the national interest growth.
DOCUMENTATION OF THE LOAN
These are the most frequently used and common documents of above mentioned charged and for other formalities for sanctioning the loan:
- Demand Promissory Note: Here the borrower promises to pay the loan as and when demanded by the bank to repay the loan.
- Letter of Arrangement: Here the written amount of the loan sanctioned to the borrower is specified.
- Letter of Continuity: It is used to take continuous facilities as providing continuous securities.
- Letter of Hypothecation: It is the written document of the goods hypothecated thus to put in case of need.
- Stock Report: This report is used for SOD and CC. In this report information about the quality and quantity of goods hypothecated have furnished.
- Personal guarantee: It is the additional confirmation of the borrower to repay.
- Guarantee of the Directors of the company.
- Resolution of the board of directors: It is used to borrow the fund to execute documents and complete other documents.
- Letter of disclaimer: By this letter, the borrower withdraws his all claim on the property/mortgaged.
- Letter of Acceptance: Letter indicating the acceptance of the sanction proposal by the borrower.
- Letter of Pledge: It is the written document of the goods pledge thus the legality of holding the goods.
- Letter of Disbursement: This is the document through which the payment of sanctioned loan indicates.
- Letter of partnership: In case of partnership firm, the partnership deeds are to be provided.
- Letter of Installment: The amount of installment that is to be paid at certain intervals.
- Tax Paying Certificate.
- Any document if described, as essential in the sanctioned advice sanctioned by the Head Office.
Recovery Performance of Janata Bank Ltd.
When Janata Bank Ltd. sanctions loans and advances to its customers, they clearly state the repayment pattern in the loan agreement. But some credit holders do not pay their credit in due period. The nationalized and private sector commercial banks have to face this sort of problems. This situation is, especially severe in Janata Bank Ltd. To overcome the problem of overdue loan, the bank need take particular loan recovery program.
RECOVERY PROGRAMS TO BE TAKEN BY JANATA BANK LTD.
- To establish credit supervision and monitoring cell in the bank
- To re-structure the loan sanctioning and distributing policy of the bank
- To sanction loans and advances against sufficient securities as best as possible
- to give more powers to the branch manager in credit management decision making process
- To offer a package of incentives to the sound borrowers
- To give more emphasis on short term loans and advances
- To impose restrictions on loans and advances for sick industries
- To take legal actions quickly against unsound borrowers as best as possible within the period specified by the law of limitations.
Credit Rating of Janata Bank Ltd.
Bangladesh Bank has made mandatory from January 2007 for all banks to have themselves credit rated by a credit rated agency vide BRPD Circular no. 6 of July 2006 for all banks. The first rating by an external independent rating agency will have to be completed by June 2007.
Accordingly Janata Bank has appointed Credit Rating Agency of Bangladesh (CRAB) to conduct Credit Rating of the bank which completed invariably by 30th June 2007. With this end and view a memorandum of understanding has been signed in between Janata Bank and CRAB on 14th May 2007.
CREDIT RATING
Credit Rating of Banks provides opinion on the types of risks associated with the relative ability of a bank for timely servicing its debts and other obligations. The rating exercise is done through a quantitative cum qualitative approach following a structured methodology.
FACTORS OF CREDIT RATING
The major factors considered in rating analysis are as follows:
Quantitative Factors:
i. Capital adequacy
ii. Assets Quality
iii. Funding & Leverage
iv. Liquidity Requirements
v. Earning Quality
vi. Market Sensitivity
Qualitative Factors
i.Owership
ii.Management Quality
iii.Risk Management
iv.Compliance with the Statutory
v.Accounting Quality
vi.Size & Market Pressure
vii. Govt. Support etc
Findings and Analysis
Every bank has its own credit procedure. Bank under study possesses a standard credit procedure. As the objective of my study is to make a comment on the credit management of Janata Bank Ltd, I try my best to collect data for the study and find out the reality. Based on the data generated during my study period I will sum up my findings here and I think this will help me to achieve my objectives.
- If we look at the historical background of Janata Bank, we see that, the objective of JBL is to earn profit as well as to improve the economic welfare of the people as a whole.
- Janata Bank Ltd. has a significant role in long term project financing in both agriculture and industrial sectors. Again JBL has a deep concern for rural farmers.
- Private sector usually concentrates in the urban areas where as public sector i.e. JBL spread their banking network all over the world.
- With a view to implementing government policies, JBL has been maintaining its position in extending credit to government bodies, sector corporations and private enterprises.
- Though bank required both quantitative and qualitative analysis but for big loans bank emphasizes on the lending risk analysis (LRA). But LRA is not a perfect measure of credit analysis. Because businessmen in our society are usually tempted to take resort of window- dressing that means accounts are so manipulated that the vital facts are concealed and facts presented are superficial. So banks have to go through both quantitative and qualitative analysis.
- According to the standard and bank’s credit procedure, credit operation is started from the customer application to the branch for the loan. But in most cases, many customers go directly to the directors of the bank and directors send them to the branch offices with his/her reference. In these cases, proper appraisal is not possible as directors the most powerful persons and bank management must give priority towards the decision of the directors. This phenomenon is very common in the bank which hampers the spontaneous procedure of credit appraisal.
- Bangladesh Bank monitors all the policies of all the private and nationalized banks of the country. According to the Bangladesh Bank’s strategy, all banks must possess the standard policies which are designed by the central bank. Janata Bank Ltd. Also possesses a standard credit proposal form. In that form all necessary information are required to fill up. But in practice credit officers do not fill up the proposal form properly. Most of the cases, they use assumption rather than exact figure. This practice might end up with bad or classified one.
- A standard policy starts from the customer’s direct application for the loan in the branch office. But it’s a common phenomenon that most of the customers directly contact with Head office and Head office choose the branch offices to disburse the loan. It hampers the normal procedure. Branches always stay under pressure when they get order for disbursement from Head office. When branches get order from the head office, then appraisal system loses its formal track. So Head office should not send any order to the branch office without prior appraisal.
- The credit management of JBL are not fully conformity with the guidelines prescribed in the bank companies Act 1991 and International Accounting Standerd-30(IAS-30)
Conclusion and recommendation
I have discussed so far about the different aspects of credit management Janata Bank Limited. For my report, I have selected Janata bank Ltd. JBL plays an important role in the banking sector as well as in our economy. The success of a bank depends largely on the efficient credit management. A successful credit management is not only need for a bank’s own performance but also it is needed for the smooth development of an economy. In any strategy of economic development, therefore, it is essential to emphasize the evaluation of a sound and well integrated credit management system from the view point of both resources mobilization and efficient allocation of funds. In conclusion it can be suggested a number of recommendations in order to overcome the problems and how to remove the causes of problem in credit management.
Since this an exploratory research, hence the recommendation given are not decisions rather they are only suggestions to improve the default rate. The recommendations are made on the basis of survey findings.
- Central Bank should take proper actions for ensuring equivalent distribution of loans and advances.
- Lending policies in our country should be geared to growth potential rather than being determined by the pre-existing collateral.
- Changes in lending policies will not suffice the purposes unless it is followed by a change in the attitude and out look of both the borrowers and the bankers.
- Improvement of credit management depends on the development of relevant, adequate, proper and reliable data base at the public sector banks as well as private sector banks in Bangladesh.
- Publishing the names of defaulter as well as good and regular payers in various dailies and granting various sorts of facilities to good borrowers will create a moral persuasion on the borrowers. This may decrease the number of defaulters and the volume of large outstanding loan amounts as well.
- Pressure from outsider and influence extorted by borrowers are also a great impediment in the smooth functioning of loan recovery process. The role of government in this case is the most important factor required to solve these sorts of problem.
- More and more competent personnel must be recruited to reduce the weakness of credit management. Competent executives will ensure the reduction of wrong appraisal and evaluation of projects.
- Prompt legal actions be taken against willful loan defaulters
- The new entrepreneurs should be encouraged in disturbing loans and those who have the records of regular payment, should be given preference.
- Steps should be taken so that guarantors cannot avoid their responsibility.
- It is observed that the defaulters generally get various sorts of exemptions as declared by the government from time to time. Government must not show any kind of mercy to the defaulters in any way which may encourage the default culture. This type of action may discourse the borrowers to become willful defaulters.
- The existing huge amount of classified loans demand for special and corrective attention for example:
- By obtaining suitable reduction on amount.
- Additional security.
- More complete financial data concerning the obligor’s condition or
- Other such action as the specific circumstances may require.
- The attempt to encourage banks to require borrowers comply with banking laws and regulations and clear up industrial properties prior to granting a loan.
- JBL should follow some straight ward mechanical procedures in assessing the risk of a borrower.
- The formulation of a sound credit policy in the possibility of default loans.
- The formulation of a sound credit policy in the banking sector as a whole has to take into account all these factors and each bank has to attempt to work out for itself what it is capable of doing so as best as possible.