CoRoT-7 is a binary star system. The star is approximately 489.2 light-years (150.0 pc) away from our Solar System. The primary, CoRoT-7A, is a G-type main-sequence star that is slightly smaller, cooler, and younger than the Sun. When compared to our Sun, it is 0.9 times more massive and 0.9 times larger. The surface temperature is 5313, and the spectral type is K0V.
The star CoRoT-7 has an apparent magnitude of 11.7 and an absolute magnitude of 5.8. It has an apparent magnitude of 11.67, making it fainter than Proxima Centauri (mag. 11.05), the closest star to the Sun. This star is located in the constellation Monoceros, approximately 520 light-years from Earth (the Unicorn).
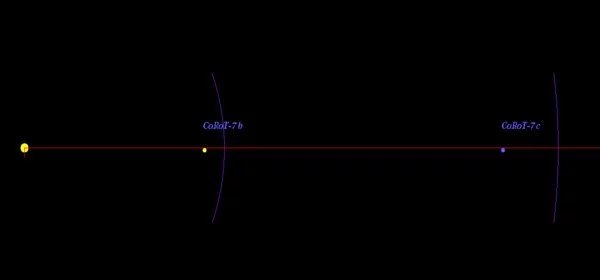
Number of Extrasolar Planets: 2. Name of the 1 Planet CoRoT-7 b radius 0.136000 mass 0.014900 orbital distance 0.017200. Name of the 2 Planet CoRoT-7 c radius 0.210839 mass 0.042660 orbital distance 0.046000. The comoving companion CoRoT-7B was discovered in 2021. It is a red dwarf star.
Location and properties
The star is in the CoRoT spacecraft’s LRa01 field of view. It is about 500 light years away from Earth. According to the project website, this field is in the Monoceros constellation. According to published data, the stellar properties are a G9V yellow dwarf with a temperature of 5250 K, a radius of about 82 percent of the Sun, and a mass of about 91 percent of the Sun. Other sources, however, have classified it as a (K0V) orange dwarf. The metallicity is 0.12 ± 0.06. The star is estimated to be about 150 parsecs away and, with an age of 1.2 – 2.3 billion years, is younger than our own star, which has an age of 4.6 billion years. The rotation period of the star, inferred by the lightcurve obtained by CoRoT, is around 23 days.
Planetary system
CoRoT-7 was discovered in 2009 by the French satellite CoRoT (Convection, Rotation, and Planetary Transits) when it passed in front of its star. CoRoT-7b orbits its star every 0.85 days at a distance of 2.6 million kilometers (1.6 million miles). It is so close to its star that its surface temperature is around 2,000 °C (3,600 °F).
The primary star is orbited by the super-Earth exoplanets CoRoT-7b and CoRoT-7c, both discovered in 2009. The existence of a possible third planet, CoRoT-7d, discovered in a published study, remains unconfirmed and doubtful. The CoRoT program used the transit method to discover the inner planet. CoRoT-7b is notable for its small size in comparison to other exoplanets known at the time.