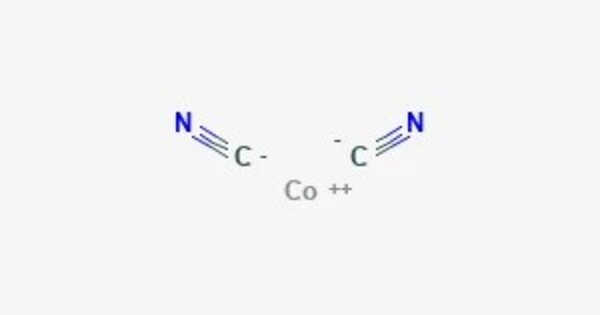
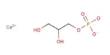
Cobalt(II) cyanide is the inorganic compound with the formula Co(CN)2. It typically forms a yellowish solid. It is soluble in water and can release cyanide ions in solution, which can be toxic. It is coordination polymer that has attracted intermittent attention over many years in the area of inorganic synthesis and homogeneous catalysis. It can form complexes with various ligands due to the coordination properties of cobalt.
Due to its toxicity, appropriate safety measures must be taken when handling cobalt(II) cyanide, including the use of personal protective equipment and proper storage protocols.
Properties
- Chemical formula: Co(CN)2
- Molar mass: 110.968 g/mol (anhydrous), 147.00 g/mol (dihydrate), 165.02 g/mol (trihydrate)
- Appearance: deep-blue powder, hygroscopic (anhydrous), reddish-brown powder (dihydrate)
- Density: 1.872 g/cm3 (anhydrous)
- Melting point: 280 °C (536 °F; 553 K) (anhydrous)
- Solubility in water: insoluble
Preparation and structure
The trihydrate salt is obtained as a reddish-brown precipitate by adding two equivalents of potassium cyanide to a cobalt salt solution:
CoCl2(H2O)6 + 2 KCN → Co(CN)2 + 2 KCl + 6 H2O
With excess cyanide, the red brown dicyanide dissolves to give pentacyanocobaltate.
Solid cobalt(II) cyanide is a coordination polymer consisting of cobalt ions linked by cyanide units in a cubic arrangement, each such cobalt atom having octahedral geometry, and an additional cobalt atom in half of the cubic cavities. That is, the structure is actually Co[Co(CN)3]2 in a zeolite-like structure. It forms hydrates and other inclusion complexes by having substances diffuse into the cavities that do not contain the cobalt atoms.
Occurrences
- Industrial Applications: Cobalt(II) cyanide is used in electroplating and as a catalyst in various chemical reactions.
- Mining and Metallurgy: It can occur as a byproduct in the processing of cobalt ores, especially in areas where cyanide is used in extraction processes.
- Laboratory: It may be synthesized in the laboratory for research purposes or in the preparation of other cobalt compounds.
Uses
Cobalt(II) cyanide has been used as a precursor to dicobalt octacarbonyl.
- Primarily used in the synthesis of other cobalt compounds.
- May have applications in electroplating and certain types of chemical reactions, but handling must be done with caution due to the toxicity of cyanide.
Safety
Cobalt(II) cyanide is toxic and poses serious health risks. Exposure can occur through inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact. Proper safety precautions, such as using personal protective equipment and working in a fume hood, are essential when handling this compound.