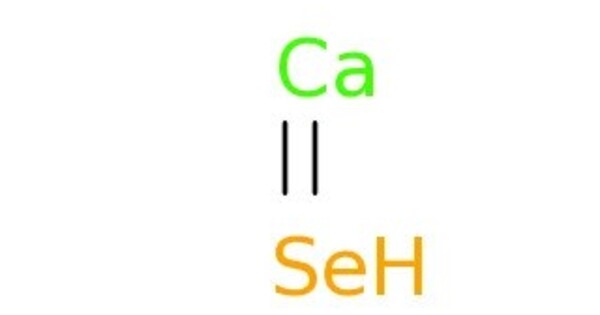
Calcium selenide (CaSe) is a chemical compound consisting of the elements calcium and selenium in equal stoichiometric ratio. It is an inorganic compound composed of calcium and selenium. It typically appears as a white or yellowish solid and is used in various applications, including:
CaSe is of interest in the field of semiconductor materials due to its electronic properties. It can be used in devices that interact with light, such as photodetectors and light-emitting devices. It serves as a source of selenium in chemical reactions or in the production of other selenium compounds.
Properties
- Chemical formula: CaSe
- Molar mass: 119.038 g/mol
- Structure: It typically crystallizes in a cubic lattice structure
- Molecular Weight: Approximately 136.96 g/mol.
- Melting Point: Around 1,075 °C (1,965 °F).
- Solubility: Insoluble in water but can dissolve in acids, forming selenide ions.
Preparation
Calcium selenide can be prepared via the reaction of calcium and H2Se in liquid NH3.
Ca + H2Se → CaSe + H2
Calcium selenide reacts with indium(III) selenide in vacuum at high temperature to give CaIn2Se4.
CaSe + In2Se3 → CaIn2Se4
Occurrences
- Natural Occurrence: Calcium selenide is not commonly found in nature as a distinct mineral but may occur in small quantities in selenium-bearing ores.
- Production: It can be synthesized through the direct combination of calcium and selenium, often in laboratory settings or for industrial purposes.
Applications
Used in the production of other selenium compounds, in semiconductor technologies, and in some photodetector materials.
Safety and Handling
Calcium selenide is considered toxic due to the presence of selenium, which can be harmful in large quantities. Proper safety precautions should be taken when handling this compound.