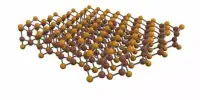
Calcium hexaboride (occasionally calcium boride) is a calcium-boron molecule having the chemical formula CaB6. It is an essential material because of its high electrical conductivity, hardness, chemical stability, and melting temperature. It’s a black, glossy, chemically inert powder with a light density. It has the cubic structure typical of metal hexaborides, with octahedral units made up of six boron atoms and calcium atoms. CaB6 and lanthanum-doped CaB6 exhibit modest ferromagnetic characteristics, which is unusual given that calcium and boron are neither magnetic nor contain inner 3d or 4f electronic shells, which are often required for ferromagnetism.
Calcium hexaboride is stable under normal conditions but can react with acids to form boric acid and calcium salts. It is not highly reactive but can interact with strong acids or oxidizing agents.
Properties
CaB6 has been studied in the past due to its unique physical features, including superconductivity, valence fluctuation, and Kondo effects. The most noteworthy feature of CaB6 is its ferromagnetism. It happens at unusually high temperature (600 K) and with low magnetic moment (less than 0.07 μB per atom). This high temperature ferromagnetism can be attributed to the ferromagnetic phase of a dilute electron gas, coupling to the postulated excitonic state in calcium boride, or external contaminants on the sample’s surface. Iron and nickel may be present as contaminants in the boron used to prepare the sample.
- Chemical formula: CaB6
- Molar mass: 104.94 g/mol
- Appearance: black powder
- Density: 2.45 g/cm3
- Melting point: 2,235 °C (4,055 °F; 2,508 K)
- Solubility in water: insoluble
- Crystal structure: Cubic
Applications
- Industrial Uses: Its hardness and stability make it useful in hard materials and cutting tools. It can also be used as a boron source in other materials.
- Electronics: Its electrical properties make it useful in certain electronic applications, including the potential for use in semiconductors.