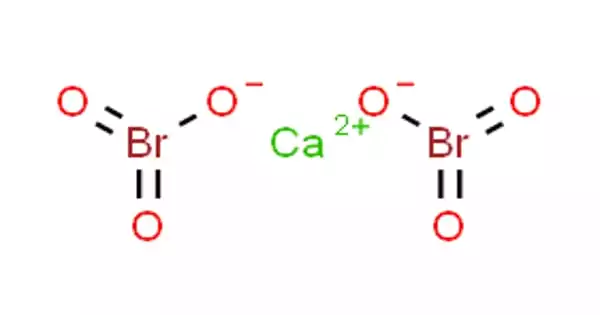
Calcium bromate, Ca(BrO3)2, is a bromic acid calcium salt. It is hygroscopic and colorless crystals with a harsh saline taste in its anhydrous form. Ca(BrO3)2•H2O is the most usually found monohydrate. One calcium atom and two bromine atoms combine to produce it.
Many reactions can occur with calcium bromide. The synthesis of calcium oxide from calcium bromide and oxygen gas is useful in the chemical industry. This reaction, which produces bromine gas at high temperatures, occurs at high temperatures.
Properties
Calcium bromide is a white hygroscopic powder that is available anhydrous. It has a density of 3.35 grams per liter and a melting point of 730 degrees Celsius. It has a boiling point of 1935 degrees Celsius. Calcium bromide is soluble in water, ethanol, methanol, and acetone, but inorganic solvents are insoluble.
- Molecular weight: 199.89 g/mol (anhydrous); 235.98 g/mol (dihydrate)
- Density: 3.353 g/cm3
- Boiling point: 1,815 °C (anhydrous); 810 °C (dihydrate)
- Melting point: 730 °C
- Appearance: White powder

Dissociation
It is a hygroscopic, colorless crystal with a harsh saline taste in its anhydrous form. It is water and alcohol-soluble. It’s made by combining calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and calcium oxide with hydrobromic acid (HBr). It can also be produced by reacting calcium metal with elemental bromine.
Preparation
Calcium hydroxide with sodium bromate or calcium sulfate with barium bromate can be used to make it. Calcium bromate decomposes over 180 °C to form calcium bromide and oxygen. Calcium bromate can theoretically be produced by the electrolysis of calcium bromide solution.
Calcium Bromate may be prepared by reacting calcium hydroxide with sodium bromate or by reacting calcium sulfate with barium bromate:
Ca(OH)2 + 2NaBrO3 → Ca(BrO3)2 + 2NaOH
CaSO4 (aq) + Ba(BrO3)2 (solid) → Ca(BrO3)2 (aq)+ BaSO4 (solid)
Of the two methods, the latter seems to be the more stable one since the temperature can be as high as 80°C in solution.
It is a chemical substance that is commonly found in drilling fluids and food preservatives. Calcium Dibromide is not harmful to any formation. It is both chemically and thermally stable. This chemical can be mixed with other solutions containing chlorides and bromides.
It is made by combining calcium carbonate CaCO3 and calcium oxide with hydrobromic acid (HBr). Calcium bromide does not occur naturally.
Application
In some countries, it is used as a bread dough and flour “improver” or conditioner. It is commonly utilized in drilling fluids as a dense aqueous solution. It is also used as a neurosis treatment, food preservatives, freezing combinations, fire retardants, and in photography.
The food industry uses this salt as a preservative and as a component of freezing mixes. It can also be used as a fire retardant, wood preservative, and dehydrating agent.
Calcium bromide is helpful in upstream oil and gas for managing wellbore pressures during completion and workover operations. Prior to burning, we spray calcium bromide on the coal to prevent mercury emissions.