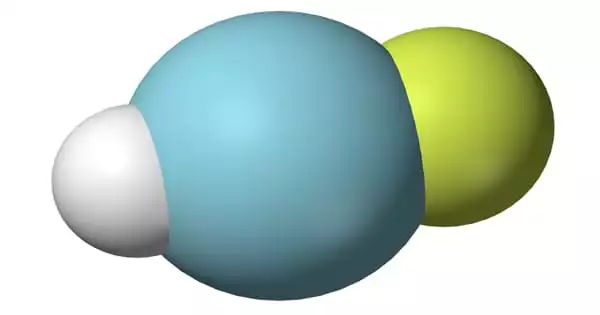
Bismuth selenide (Bi2Se3) is a gray compound of bismuth and selenium also known as bismuth(III) selenide. It is a compound that has gained attention for its unique properties, particularly in the realm of materials science and condensed matter physics. It’s a type of topological insulator, which means it has insulating bulk properties but conducts electricity on its surface.
Bismuth selenide also has promising thermoelectric properties, meaning it can convert heat into electrical energy and vice versa. This makes it useful for applications in power generation and refrigeration.
Properties
Bismuth selenide is a semiconductor and a thermoelectric material. As a topological insulator, it has surface states that are protected by time-reversal symmetry. These surface states are robust against impurities and imperfections, making them of interest for various applications in electronics and quantum computing.
- Chemical formula: Bi2Se3
- Molar mass: 654.8 g/mol
- Appearance: Dull grey
- Density: 6.82 g/cm3
- Melting point: 710 °C (1,310 °F; 983 K)
- Solubility in water: insoluble
- Solubility: insoluble in organic solvents
Bismuth selenide occurs naturally in very small quantities, typically associated with other selenium and bismuth minerals. It is not found in large deposits but rather as a minor component in certain mineral deposits.
Production
Although bismuth selenide occurs naturally (as the mineral guanajuatite) at the Santa Catarina Mine in Guanajuato, Mexico as well as some sites in the United States and Europe, such deposits are rare and contain a significant level of sulfur atoms as an impurity. For this reason, most bismuth selenide used in research into potential commercial applications is synthesized. Commercially-produced samples are available for use in research, but the concentration of selenium vacancies is heavily dependent upon growth conditions, and so bismuth selenide used for research is often synthesized in the laboratory.
Applications
Due to its topological surface states, bismuth selenide is being studied for potential use in spintronic devices, which utilize the spin of electrons for information processing. It’s also being explored in the context of quantum computing and other advanced technologies.