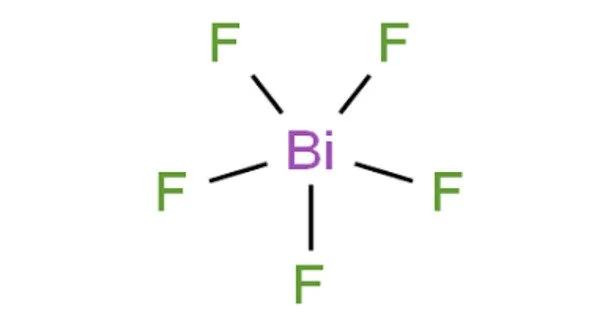
Bismuth pentafluoride, sometimes known as BiF5, is an inorganic chemical with the formula BiF5. It is a bismuth coordination entity and a pnictogen halide. It is a white solid with high reactivity. It is derived from a bismuthorane hydride. Researchers are interested in the chemical, but it is not particularly valuable.
Properties
- Chemical formula: BiF5
- Molar mass: 303.97 g mol−1
- Appearance: long white needles, colorless crystalline solid
- Density: 5.40 g cm−3
- Melting point: 151.4 °C (304.5 °F; 424.5 K) , 154.4 °C
- Boiling point: 230 °C (446 °F; 503 K)
Structure
BiF5 is polymeric and consists of linear chains of trans-bridged corner-sharing BiF6 octahedra. This is the same structure as α-UF5.
Preparation
Bismuth pentafluoride is generally prepared by heating bismuth trifluoride with F2 or ClF3.
BiF5 can be prepared by treating BiF3 with F2 at 500 °C.
BiF3 + F2 → BiF5
In an alternative synthesis, ClF3 is the fluorinating agent at 350 °C.
BiF3 + ClF3 → BiF5 + ClF
Purification
Sublimation under vacuum at roughly 1000C in an apparatus composed entirely of Vycor glass, which is not affected by bismuth pentafluoride, can be used to purify bismuth pentafluoride. Prior to usage, bismuth pentafluoride can be crystallized from anhydrous HF.
Reactions
Bismuth pentafluoride is the most reactive of the pnictogen pentafluorides and a highly effective fluorinating agent. At room temperature, it interacts vigorously with water to generate ozone and oxygen difluoride, as well as with iodine or sulfur. Above 50 °C, BiF5 fluorinates paraffin oil (hydrocarbons) to fluorocarbons and oxidises UF4 to UF6. Bismuth pentafluoride fluorinates Br2 to BrF3 and Cl2 to ClF at 180 °C.
BiF5 also reacts with alkali metal fluorides, MF, to form hexafluorobismuthates, M[BiF6], containing the hexafluorobismuthate anion, [BiF6]−.
Safety
Bismuth pentafluoride is moisture sensitive. It should be kept in a firmly closed container in a dry environment. Bismuth pentafluoride can irritate the eyes, skin, digestive tract, and respiratory tract. Bismuth pentafluoride’s toxicological qualities have not been thoroughly studied.