A biogeographic realm is the broadest biogeographic division of the Earth’s land area based on terrestrial creature distribution patterns. It is a huge geographical area characterized by a distinct collection of plant and animal species and their ecosystems. It is also known as an ecozone or biogeographic region. They are further classified into bioregions, which are broken further into ecoregions.
A biogeographic realm is also referred to as a “ecozone,” albeit this term can also refer to ecoregions. These domains are determined by species distribution patterns and evolutionary history, as well as environmental elements like climate, geology, and geography. Alfred Russel Wallace began developing a concept of zoogeographic regions in 1872, expanding on ornithologist Philip Sclater’s six-region approach.
Description
The realms are huge sections of the Earth’s surface where creatures evolved in relative isolation over long periods of time, separated by physical features such as oceans, broad deserts, or steep mountain ranges that act as natural barriers to migration. As a result, biogeographic realm designations are used to identify broad groups of organisms based on their common biogeography. Biogeographic realms are analogous to floristic kingdoms in botany and zoogeographic regions in zoology.
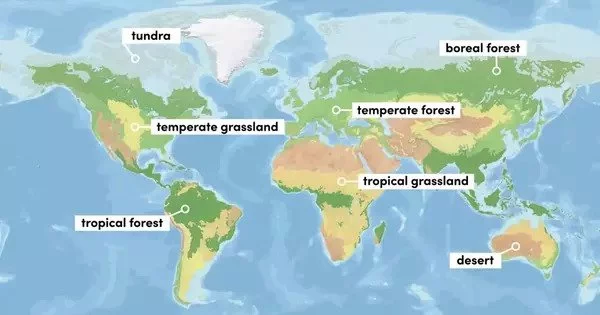
On Earth, there are several distinct biogeographic realms, each with its own variety of flora and fauna. The number and borders of these domains vary depending on the classification system employed, but the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) devised a widely accepted framework. The WWF’s classification includes the key biogeographic realms listed below:
- Nearctic Realm: Except for the high Arctic and the majority of Mexico, this area encompasses North America. It is distinguished by the presence of animals such as bison, grizzly bears, and bald eagles.
- Palearctic Realm: This domain, which includes Europe, Asia north of the Himalayas, and northern Africa, is noted for creatures such as brown bears, wolves, and several deer species.
- Neotropical Realm: Also referred to as the Neotropic or Neotropical, this realm covers Central and South America. It is rich in biodiversity, with iconic species like jaguars, sloths, and macaws.
- Afrotropical Realm: This realm includes most of Africa south of the Sahara Desert and is home to diverse wildlife, including African elephants, lions, and giraffes.
- Indomalayan Realm: This region, which includes South and Southeast Asia, is noted for its tropical rainforests and distinctive animals such as Bengal tigers, orangutans, and Asian elephants.
- Australasian Realm: Australia, New Guinea, and surrounding islands are included in this domain. It is home to a diverse range of marsupials, including as kangaroos and wallabies.
- Oceania Realm: The Oceania realm encompasses the Pacific Ocean’s islands, including Hawaii, Fiji, and other islands. It is well-known for its marine biodiversity and one-of-a-kind island species.
Biogeographic realms provide a framework for understanding the distribution of species and ecosystems around the world, and they play an important role in conservation efforts by identifying high biodiversity areas and prioritizing conservation initiatives.