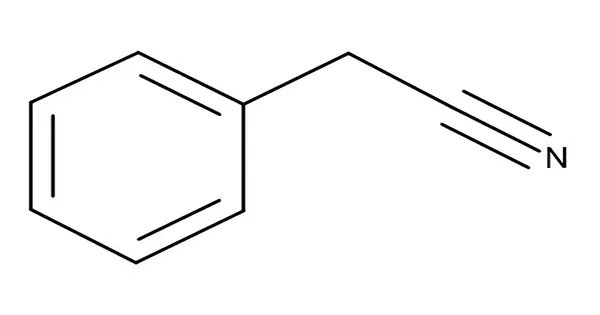
Benzyl cyanide (abbreviated BnCN) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH2CN. This colorless oily aromatic liquid is an important precursor to numerous compounds in organic chemistry. It is also an important pheromone in certain species. It is important to handle benzyl cyanide with care and ensure proper protective equipment is used when working with it due to its toxic and flammable nature.
Preparation
Benzyl cyanide can be produced via Kolbe nitrile synthesis between benzyl chloride and sodium cyanide and by oxidative decarboxylation of phenylalanine.
Benzyl cyanides can also be prepared by arylation of silyl-substituted acetonitrile.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C8H7N
- Molar mass: 117.15 g/mol
- Appearance: Colorless oily liquid
- Density: 1.015 g/cm3
- Melting point: −24 °C (−11 °F; 249 K)
- Boiling point: 233 to 234 °C (451 to 453 °F; 506 to 507 K)
Reactions
Benzyl cyanide undergoes many reactions characteristic of nitriles. It can be hydrolyzed to give phenylacetic acid or it can be used in the Pinner reaction to yield phenylacetic acid esters. Hydrogenation gives β-phenethylamine.
It can undergo hydrolysis (reaction with water) to form benzylamine and formic acid, or it can be further transformed into other compounds like benzyl isocyanide (also known as isonitrile). The compound contains an “active methylene unit”. Bromination occurs gives PhCHBrCN. A variety of base-induced reactions result in the formation of new carbon-carbon bonds.
Uses
Benzyl cyanide is used as a solvent and as a starting material in the synthesis of fungicides (e.g. Fenapanil), fragrances (phenethyl alcohol), antibiotics, and other pharmaceuticals. The partial hydrolysis of BnCN results in 2-phenylacetamide.
- Chemical Synthesis: Benzyl cyanide is often used as an intermediate in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other fine chemicals. It’s particularly involved in the synthesis of certain types of benzyl-based compounds.
- Preparation of Benzylamine: It is used in the preparation of benzylamine, which is used as a precursor for manufacturing various chemicals.
- Fragrance Industry: Its almond-like odor makes it a component in some perfumes and flavorings, although it is used in limited quantities due to its toxicity.
- Production of Other Nitriles: It can be involved in reactions to produce other nitriles, such as benzyl isocyanide.
Safety and Hazards
- Toxicity: Benzyl cyanide is toxic, as it contains a nitrile group that can release cyanide ions. It should be handled with care to avoid inhalation or skin contact.
- Flammability: It is flammable and should be kept away from open flames or heat sources.
- Cyanide Poisoning: Due to the presence of the nitrile group, benzyl cyanide can release cyanide upon hydrolysis, posing a significant health risk.
Occurrence
Benzyl cyanide does not naturally occur in significant quantities but can be synthesized in the laboratory or industrially.