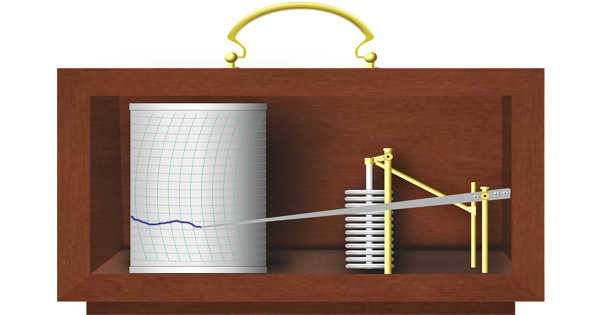
A barograph is a type of barometer that graphically records the barometric pressure over time. It’s a self-contained aneroid barometer. It is a recording aneroid barometer that records changes in atmospheric pressure on chart paper. This device is also used to continuously record atmospheric pressure.
A barograph chart is attached to a drum that is normally turned by clockwork. The pressure-sensitive element, a partially evacuated metal cylinder, is connected to a pen arm in such a way that the pen’s vertical displacement is proportional to changes in atmospheric pressure. The ink trace, or barogram, on the recording paper, serves as a visual record of pressure changes. The barogram trend shown here can be extremely useful in forecasting weather changes.
The pressure-sensitive element, a partially evacuated metal cylinder, is connected to a pen arm in such a way that the pen’s vertical displacement is proportional to changes in atmospheric pressure. The pen makes a record of pressure versus time on a chart, which is mounted on a clockwork-turned drum. Each chart usually contains one week’s worth of data.
The barograph is an instrument that aids in the continuous measurement of atmospheric pressure values. The barograph is the device used to record the values obtained by the barometer. This device is integrated into the barograph, and the readings are obtained without the use of mercury. It is based on the reading obtained by crushing thin layers of metal as a cylindrical shape caused by atmospheric pressure.

Modern Use
Atmospheric pressure is an important factor to consider in meteorology if we want to make accurate predictions and study the behavior of the climate. Changes in atmospheric pressure influence all atmospheric and meteorological phenomena.
Traditional recording barographs for meteorological use have been largely replaced (though not entirely) by electronic weather instruments that record barometric pressure using computer methods. These are not only less expensive than previous barographs, but they may also offer greater recording length and the ability to perform additional data analysis on the captured data, including automated weather forecasting. Collectors prize older mechanical barographs because they make excellent display pieces and are often made of high-quality wood and brass.
Barographs can be used to record elevation changes during an aircraft flight because atmospheric pressure responds predictably to changes in altitude. The FAI required barographs to record certain tasks and attempts associated with sailplanes. A continuously varying trace indicated that the sailplane had not landed during a task, whereas measurements from a calibrated trace could be used to determine completion of altitude tasks or record setting.