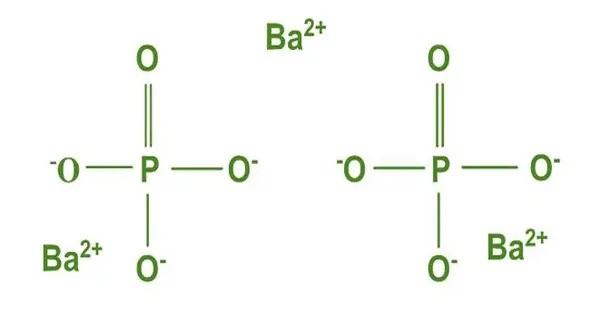
Barium phosphate (also known as barium orthophosphate) is an inorganic phosphate of barium with the molecular formula Ba3(PO4)2. It is an inorganic compound composed of barium and phosphate ions. It appears as a white, odorless powder and is insoluble in water but soluble in acidic solutions. It is usually found as a white, odorless powder which is insoluble in water.
Barium phosphate is primarily used in ceramics, glass manufacturing, and as a component in phosphor coatings for fluorescent lamps. It is also studied for potential applications in biomaterials and bone grafts due to its biocompatibility. The compound is typically synthesized by reacting barium salts (like barium chloride) with phosphates (such as sodium phosphate).
Preparation
The general chemical reaction for the preparation of barium phosphate powder is:
Ba(NO3)2 + 2NH4H2PO4 → Ba3(PO4)2 + 2NH4NO3 + 4HNO3
It is stable under normal conditions but should be handled carefully, as barium compounds can be toxic if ingested or inhaled in large amounts. Proper protective equipment is recommended during handling.
Structure
Its crystal structure is rhombohedral with a space group of R3m, the same as in strontium phosphate.
Properties
Barium phosphate exhibits properties such as high refractive index, low melting and low glass transition temperature, high transparency to ultraviolet light, and high thermal expansion coefficient.
- Chemical formula: Ba3(PO4)2
- Molar mass: 601.9 g/mol
- Appearance: White powder or crystals
- Solubility in water: Insoluble
- Solubility in acids: Soluble in dilute acids
- Density: ~4.1 g/cm³
- Melting point: > 1000 °C (decomposes)
- Odor: Odorless
- Crystal system: Triclinic or monoclinic (depends on polymorph)
Applications
- Used in the production of specialty glasses and ceramics.
- Acts as a fluxing agent in enamels and glazes.
- Sometimes used in phosphate coatings for metal surfaces.
- Laboratory reagent in analytical chemistry.
Natural Occurrence
- Not commonly found in nature as pure barium phosphate.
- May occur in trace amounts in mineral form, typically in association with other barium-containing minerals.
- No significant naturally occurring mineral is composed primarily of Ba₃(PO₄)₂.
Safety and Handling
- Toxicity: Contains barium, which is toxic if ingested in soluble forms. However, barium phosphate is relatively insoluble and less bioavailable.
- Precautions: Use gloves and eye protection; avoid inhalation of dust.
- Environmental Impact: Insoluble, but disposal should avoid release into water systems due to barium content.