It typically appears as a white to yellowish crystalline solid. It moderately soluble in organic solvents like ethanol and acetone, but insoluble in water. It varies depending on hydration and impurities, but it typically melts around 200 °C. Generally stable under normal conditions; however, it can decompose upon heating or when exposed to strong acids.
Properties
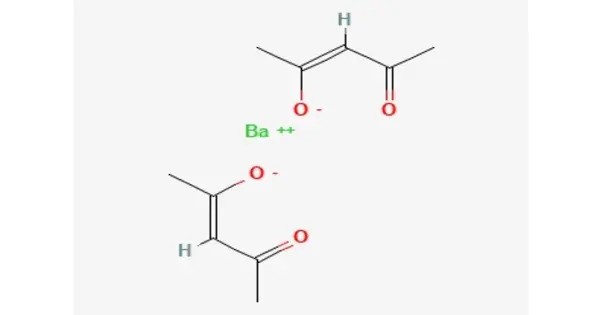
- Chemical formula: C10H14BaO4
- Molar mass: 335.545 g·mol−1
- Appearance: White solid
- Solubility: Moderately soluble in organic solvents, but poorly soluble in water.
- Melting Point: Generally varies with specific forms, but can decompose rather than melt.
Uses
Barium acetylacetonate has been examined in metal organic chemical vapour deposition of BaTiO3 thin films. The related complex with hexafluoroacetylacetonate Ba(hfa)2(tetraglyme) has also been investigated. Its formation of a sublimable adduct containing a polyether illustrates the high coordination numbers typical of barium.
- Catalyst: It can act as a catalyst in various organic reactions.
- Precursor: Used in the preparation of barium-containing materials, such as ceramics and luminescent materials.
Safety and Handling
Barium compounds can be toxic, especially if ingested or inhaled. Appropriate safety measures, such as gloves and goggles, should be used when handling this compound.