Analysis Of Financial Performance Of Summit Power Limited (SPL)
Summit Power Limited (SPL), sponsored by Summit Industrial and Mercantile Corporation (SIMCL), is the first Bangladeshi Independent Power Producer (IPP) in private sector of Bangladesh which is providing power to national grid. SPL was incorporated in Bangladesh on March 30, 1997 as a Private Limited Company. On June 7, 2004 the Company was converted to Public Limited Company under the Companies Act 1994.
Summit Power Limited in 2001, has successfully established three power plants of 11 MW capacity each, for sale of electricity to Rural Electrification Board (REB) on Build, Own and Operate basis at Savar, Narsingdi and Comilla. During 2006 and 2007 in each of the above three places, 2nd unit was commissioned enhancing the capacity of SPL to 105 MW. In 2009 SPL with its 99% owned two subsidiaries has established 4 new power plants raising its capacity to 215 MW. In 2011 SPL has commissioned another power plant of 102 MW capacities at Narayanganj under Summit Narayanganj Power Limited, where SPL has 55% ownership.
SUMMIT POWER LIMITED AT A GLANCE
With a view to materialize the dream of the people of Bangladesh for receiving uninterrupted electricity, a group of highly successful entrepreneurs conceived an idea of floating a power production company styled as “Summit Power Limited” which is named as a desire that the company will grow to the highest peaks of the world. The sponsors are reputed personalities in the field of trade & commerce, industry and finance. “Summit Power Limited” offers the full range of power production facility. There is no diversification of services as it is solely an independent power production company. The company is being managed by a group of highly experienced professionals with diversified experience in finance and managing. The Management of the company constantly looks after POWER LTD. The company has already achieved tremendous progress within only eight years. The company has already ranked as one of the quality power producers & is known for its reputation. It offers the full range of power production services for government, covering all segments of society within the framework of public companies Act and rules and regulations laid down by our government.
By now, the company established correspondent relationship with 18 Banks covering their global network of 385 branches/units of International repute at different important locations. It also established accounting relationship with 10 Banks and maintaining 60 Accounts in 3 (three) major Currencies at different convenient locations.
The Board of Directors of the company consists of reputed Industrialists and Businessmen who are successful in their respective fields headed by Mr. Muhammed Aziz Khan, the Chairman of the Board who is an eminent Industrialist & reputed businessman in Bangladesh and founder president of Bangladesh Energy Companies Association (BECA). The Board generally deals with policy matters relating to management of Business and sets goal for the growth & development of the company as a whole, review of the same from time to time and gives necessary guidance to the management.
The company is managed by a Team of professional Executives and Officials having profound knowledge & expertise in different areas of management and operation of the company.
During the short span of time, Summit Power Limited has so far introduced a good number of power plants to broaden the resource base and develop the power sector of the country. Some more plants will be introduced gradually in near future suiting to the requirement of the clients, BPDB and REB. Since inception, The Company has been performing very well in the production of electricity.
All activities of the company including its power generation are mainly for different economic groups of Bangladesh.
SUMMIT POWER LIMITED PROJECTS
ASHULIA POWER PLANT
This project was set up to provide electricity for Dhaka PalliBidyutSamity under 15-years Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) with Rural Electrification Board (REB). An implementation agreement has also been signed with the government of Bangladesh (GoB).
After signing expansion agreements with REB and GoB, Summit Power has increased this plant’s capacity by 33.75 MW with the total output being 45 MW.
NARSINGDI POWER PLANT
This project was set up to provide electricity for NarsingdiPalliBidyutSamity under 15- years Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) with Rural Electrification Board (REB). An implementation agreement has also been signed with the government of Bangladesh (GoB).
After signing expansion agreements with REB and GoB, Summit power has increased this plant’s capacity by 24.30 MW with the total output being 35 MW.
COMILLA POWER PLANT
This project was set up to provide electricity for ComillaPalliBidyutSamity under 15- years Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) with Rural Electrification Board (REB). An implementation agreement has also been signed with the government of Bangladesh (GoB). After signing expansion agreements with REB and GoB, Summit power has increased this plant’s production capacity by 13.50 MW with the total output being 25 MW.
SUMMIT UTTARANCHOL POWER COMPANY LIMITED PROJECTS
ULLAPARA POWER PLANT
This project was set up to provide electricity for SirajganjPalliBidyutSamity under 15- years Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) with Rural Electrification Board (REB). An implementation agreement has also been signed with the government of Bangladesh (GoB). The total output being 11 MW.
MAONA POWER PLANT
This project was set up to provide electricity for Maymensingh and GazipurPalliBidyutSamity under 15-years Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) with Rural
Electrification Board (REB). An implementation agreement has also been signed with the government of Bangladesh (GoB). The total output being 33 MW.
SUMMIT PURBANCHOL POWER COMPANY LIMITED PROJECTS
JANGALIA POWER PLANT
This project was set up to provide electricity for Comilla Grid Substation under 15-years Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) with Bangladesh Power Development Board (BPDB). An implementation agreement has also been signed with the government of Bangladesh (GoB). The total output being 33 MW.
RUPGANJ POWER PLANT
This project was set up to provide electricity for NarayanganjPalliBidyutSamity under 15-years Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) with Rural Electrification Board (REB). An implementation agreement has also been signed with the government of Bangladesh (GoB). The total output being 33 MW.
SUMMIT NARAYANGANJ POWER LIMITED PROJECT
MADANGANJ POWER PLANT
This project was set up to provide electricity to Bangladesh Power Development Board (BPDB) under Build, Own and Operate (BOO) basis using Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO). The entire generated electricity will be sold to BPDB. The total output being 102 MW.
I. ADMIN & HR DEPARTMENT
Admin and HR department handles the recruiting of new employees and other daily administrative activities.
II. ACCOUNTS DEPARTMENT
Accounts department handles the daily cash transactions, receives cheques from the customers and provides cheques to the suppliers of different items.
III.COMMERCIAL DEPARTMENT
Commercial department generally handles LC opening and other LC related stuff. They are the key department for importing any parts of the engines or importing engines from abroad for operation.
IV.DEVELOPMENT DEPARTMENT
Development department works for new projects or for development of existing project. They make bidding proposal when there is any new project and submits the proposal to the government to get the project.
V.IT DEPARTMENT
IT department maintains and operates the websites of the company over the internet. They keep the website up to date with the operations of the company. Whenever there is new news or information, it is uploaded in the website by IT department.
VI.TRAINING DEPARTMENT
Generally training is conducted by Admin & HR department in other companies but in Summit Power Limited has an individual department that handles the training activities of different employees according to the need.
INTRODUCTION TO THE REPORT
The importance of electricity for the economic development of Bangladesh has received so much attention in the recent times that efforts from all quarters are now concentrated as to what can be done to improve the current power crisis. Failure in the generation of electricity in the past years due to poor planning and inappropriate utilizing of the already generated electricity has been the key impediment in the development of the energy sector of Bangladesh.
As part of the government’s initiative to increase the generation of electricity in the country and to solve the reeling power crisis, the purchase committee of the government has recently approved proposals of five lowest bidders to generate over 200 Megawatts (MW) of electricity across the country for installation of power plants in the private sector.
OBJECTIVES OF THE REPORT
Every study should be equipped with some objectives. Here the following objectives, which were considered to carry out the report. These objectives are as follows but not limited to these only –
- Assessment Of Past Performance
Past performance is a good indicator of future performance. Investors or creditors are interested in the trend of past sales, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, net income, cash flows and return on investment. These trends offer a means for judging management’s past performance and are possible indicators of future performance.
- Assessment of current position
Financial statement analysis shows the current position of the firm in terms of the types of assets owned by a business firm and the different liabilities due against the enterprise.
- Prediction of profitability and growth prospects
Financial statement analysis helps in assessing and predicting the earnings prospects and growth rates in earning which are used by investors while comparing investment alternatives and other users in judging earning potential of business enterprise.
- Prediction of bankruptcy and failure
Financial statement analysis is an important tool in assessing and predicting bankruptcy and probability of business failure.
- Assessment of the operational efficiency
Financial statement analysis helps to assess the operational efficiency of the management of a company. The actual performance of the firm which are revealed in the financial statements can be compared with some standards set earlier and the deviation of any between standards and actual performance can be used as the indicator of efficiency of the management.
SCOPE OF THE REPORT
This report has been prepared based on Power sector business considering over all power sector condition of Bangladesh. This study makes attempt to cover but not limited to the Financial Area of Summit Power Limited. An effort to depict the overall performance (Financial and Non-financial) has been made to make the report a comprehensive one.
DATA COLLECTION
Primary Data
In this regards, primary data was collected by interviewing personnel from different departments. Sometimes, different personnel from the customers (Bangladesh Power Development Board – BPDB) were also interviewed.
Secondary Data
Different Finance and Accounting books, journals, annual reports and websites were used for Secondary data collection. Some publications from the Government and other parties were great interests.
TURNOVER/ REVENUE
In business, turnover or revenue is income that a company receives from its normal business activities, usually from the sale of goods and services to customers. Some companies receive revenue from interest, royalties, or other fees. Revenue may refer to business income in general, or it may refer to the amount, in a monetary unit, received during a period of time. Profits or net income generally imply total revenue minus total expenses in a given period. In accounting, revenue is often referred to as the “top line” due to its position on the income statement at the very top. This is to be contrasted with the “bottom line” which denotes net income.
In more formal usage, revenue is a calculation or estimation of periodic income based on a particular standard accounting practice or the rules established by a government or government agency. Revenue is a crucial part of financial statement analysis. A company’s performance is measured to the extent to which its asset inflows (revenues) compare with its asset outflows (expenses). Net Income is the result of this equation, but revenue typically enjoys equal attention during a standard earnings call. If a company displays solid “top-line growth,” analysts could view the period’s performance as positive even if earnings growth, or “bottom-line growth” is stagnant. Conversely, high net income growth would be tainted if a company failed to produce significant revenue growth. Consistent revenue growth, if accompanied by net income growth, contributes to the value of an enterprise and therefore the stock price.
Revenue is used as an indication of earnings quality. There are several financial ratios attached to it, the most important being gross margin and profit margin. Also, companies use revenue to determine bad debt expense using the income statement method.
GROSS PROFIT
In accounting, gross profit or sales profit is the difference between revenue and the cost of making a product or providing a service, before deducting overhead, payroll, taxation, and interest payments. This is different from operating profit (earnings before interest and taxes).
The various deductions (and their corresponding metrics) leading from Net sales to Net income are as follow:
Net sales = Gross sales – (Customer Discounts, Returns, Allowances)
Gross profit = Net sales – Cost of goods sold
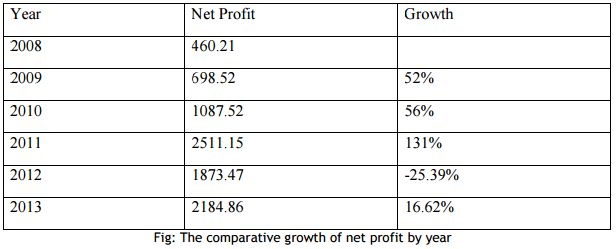
NET PROFIT
Net profit is referred to as the bottom line, net income, or net earnings is a measure of the profitability of a venture after accounting for all costs. In accounting, net profit is equal to the gross profit minus overheads minus interest payable for a given time period (usually: accounting period).
In simplistic terms, net profit is the money left over after paying all the expenses of an endeavor. In practice this can get very complex in large organizations or endeavors. The bookkeeper or accountant must itemize and allocate revenues and expenses properly to the specific working scope and context in which the term is applied.
How does a company decide whether it is successful or not, is probably the most common way is to look at the net profits of the business. Given that companies are collections of projects and markets, individual areas can be judged on how successful they are at adding to the corporate net profit.
To calculate net profit for a venture, subtract all costs, including a fair share of total corporate overheads, from the gross revenues or turnover.
Net profit = Sales revenue – Total costs
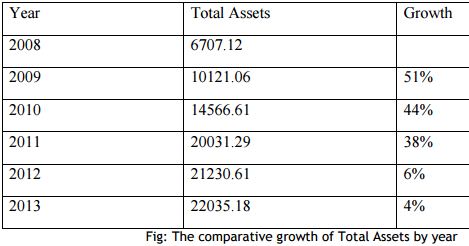
TOTAL ASSETS
An asset is a resource controlled by the entity as a result of past events or transactions (verification needed) and from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the entity.
In financial accounting, assets are economic resources. Anything tangible or intangible that is capable of being owned or controlled to produce value and that is held to have positive economic value is considered an asset. Simply stated, assets represent value of ownership that can be converted into cash (although cash itself is also considered an asset).
The balance sheet of a firm records the monetary value of the assets owned by the firm. It is money and other valuables belonging to an individual or business. Two major asset classes are tangible assets and intangible assets. Tangible assets contain various subclasses, including current assets and fixed assets. Current assets include inventory, while fixed assets include such items as buildings and equipment. Intangible assets are nonphysical resources and rights that have a value to the firm because they give the firm some kind of advantage in the market place.
In the financial accounting sense of the term, it is not necessary to be able to legally enforce the asset’s benefit for qualifying a resource as being an asset, provided the entity can control its use by other means. The accounting equation relates assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity:
Assets = Liabilities + Stockholder’s Equity (Owner’s Equity)
Assets = liabilities + Capital
liabilities = Assets – Capital
Capital = Assets – liabilities
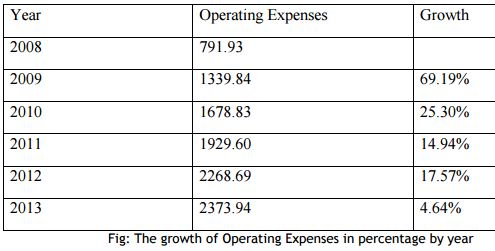
OPERATING EXPENSES
Operating Expenses is a category of expenditure that a business incurs as a result of performing its normal business operations. One of the typical responsibilities that management must contend with is determining how low operating expenses can be reduced without significantly affecting the firm’s ability to compete with its competitors.
In business, an operating expense is a day-to-day expense such as sales and administration, or research & development, as opposed to production, costs, and pricing. In short, this is the money the business spends in order to turn inventory into throughput.
On an income statement, “operating expenses” is the sum of a business’s operating expenses for a period of time, such as a month or year.
In TOC, operating expense is limited to costs that vary strictly with the quantity produced, like raw materials and purchased components. Everything else is a fixed cost, including labor (unless there is a regular and significant chance that workers will not work a full-time week when they report on its first day).
In a real estate context, operating expenses include costs associated with the operation and maintenance of an income-producing property.
PAID-UP CAPITAL
The amount of a company’s capital that has been funded by shareholders is called Paid-up Capital. Paid-up capital can be less than a company’s total capital because a company may not issue all of the shares that it has been authorized to sell. Paid-up capital can also reflect how a company depends on equity financing.
It is the total amount of shareholder capital that has been paid in full by shareholders or the amount of money that has been received by shareholders who have completely paid for their purchased shares. This would not include any shares that have been bid on, but not yet purchased.
In other words Paid-up or Subscribed capital is the amount of capital (out of authorized capital) for which company has received applications from the general public who are interested in buying shares. If this term is too technical to be understood then subscription is simply an application in which investors expresses his interest to buy shares in the company.
Usually only that much shares are subscribed which company intends to issue later. But sometimes, if company is in good shape then more and more people will be interested in buying shares and in this case over-subscription will be the result. But if company’s financial position is not sound or due to other factors it may be possible that subscriptions are received for lesser then intended shares in which case there will be under-subscription.
CURRENT ASSET
In accounting, a current asset is an asset which can either be converted to cash or used to pay current liabilities within 12 months. Typical current assets include cash, cash equivalents, short-term investments, accounts receivable, inventory and the portion of prepaid liabilities which will be paid within a year. On a balance sheet, assets will typically be classified into current assets and long-term assets.
A balance sheet account that represents the value of all assets that are reasonably expected to be converted into cash within one year in the normal course of business is Current Asset. Current assets include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, marketable securities, prepaid expenses and other liquid assets that can be readily converted to cash. In personal finance, current assets are all assets that a person can readily convert to cash to pay outstanding debts and cover liabilities without having to sell fixed assets. According to the IFRS Current assets include – Current inventories, Trade and other current receivables, Current tax assets, Current biological assets, Other current financial assets, Other current non-financial assets, Cash and cash equivalents and so on.
It expects to realize the asset, or intends to sell or consume it, in its normal operating cycle; it holds the asset primarily for the purpose of trading; it expects to realize the asset within twelve months after the reporting period; or the asset is cash or a cash equivalent unless the asset is restricted from being exchanged or used to settle a liability for at least 12 months after the reporting period.
CURRENT LIABILITY
Company’s debts or obligations those are due within one year. Current liabilities appear on the company’s balance sheet and include short term debt, accounts payable, accrued liabilities and other debts.
In accounting, current liabilities are often understood as all liabilities of the business that are to be settled in cash within the fiscal year or the operating cycle of a given firm, whichever period is longer. A more complete definition is that current liabilities are obligations that will be settled by current assets or by the creation of new current liabilities.
The proper classification of liabilities provides useful information to investors and other users of the financial statements. It may be regarded as essential for allowing outsiders to consider a true picture of an organization’s fiscal health.
One application is in the current ratio, defined as the firm’s current assets divided by its current liabilities. A ratio higher than one means that current assets, if they can all be converted to cash, are more than sufficient to pay off current obligations. All other things equal, higher values of this ratio imply that a firm is more easily able to meet its obligations in the coming year.
SHAREHOLDERS EQUITY
A firm’s total assets minus its total liabilities are the Shareholders’ Equity. Equivalently, it is share capital plus retained earnings minus treasury shares. Shareholders’ equity represents the amount by which a company is financed through common and preferred shares.
In accounting and finance, equity is the residual claim or interest of the most junior class of investors in assets, after all liabilities are paid. If liability exceeds assets, negative equity exists. In an accounting context, Shareholders’ equity (or stockholders’ equity, shareholders’ funds, shareholders’ capital or similar terms) represents the remaining interest in assets of a company, spread among individual shareholders of common or preferred stock.
At the start of a business, owners put some funding into the business to finance operations. This creates a liability on the business in the shape of capital as the business is a separate entity from its owners. Businesses can be considered, for accounting purposes, sums of liabilities and assets; this is the accounting equation. After liabilities have been accounted for, the positive remainder is deemed the owner’s interest in the business.
This definition is helpful in understanding the liquidation process in case of bankruptcy. At first, all the secured creditors are paid against proceeds from assets. Afterward, a series of creditors, ranked in priority sequence, have the next claim/right on the residual proceeds.
Ownership equity is the last or residual claim against assets, paid only after all other creditors are paid. In such cases where even creditors could not get enough money to pay their bills, nothing is left over to reimburse owners’ equity. Thus owners’ equity is reduced to zero. Ownership equity is also known as risk capital or liable capital.
TREND ANALYSIS
The trend analysis of a company evaluates the financial information over some specific period of time. This is typically shown as a dollar amount change and a percentage change over years. The objective is to calculate and study the amount change and percent change from one period to the next. The percent change is calculated as follows:
Percent change = (Current year amount – Base year amount) ÷ Base year amount
Now, the trend analysis of six consecutive years and their interpretations are given below.
FOR THE YEAR 2011-2010
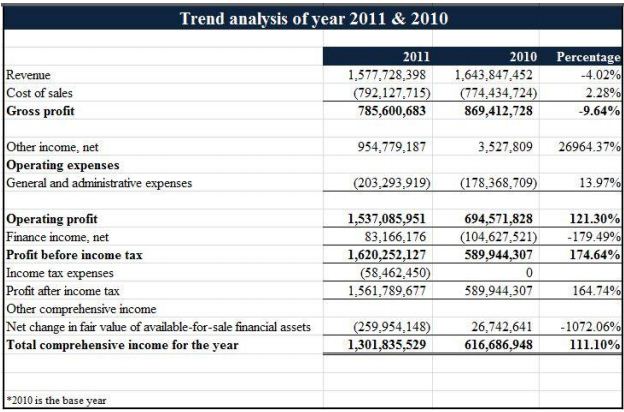
This data set shows that the revenue initially decreased by 4.02%. Cost of sales had an increase of 2.28%, means their cost increased a little bit. After that, the decrease in revenue and related increase in cost of sales resulted in a gross loss of 9.64%.
The increase in general and administrative expenses was13.97%.Their massive increase in operating profit was121.30%. After deducting the net income, we find that the profit before paying income tax is 174.64% which is tremendously higher than previous year.
After deducting the taxes and the net price of all the financial assets, there was an increase in the total comprehensive income of111.10%, meaning their company was running smoothly without much of any ups and downs.
FOR THE YEAR 2013-2012
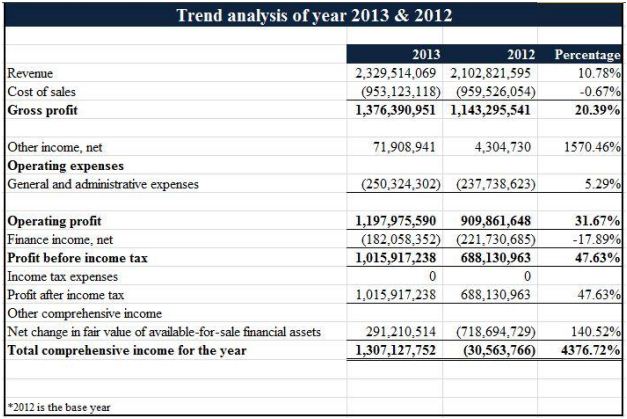
This analysis shows that the revenue increased by 10.78%. Cost of goods sold had a corresponding increase of 0.67%, means costsomewhat increased. Then again, the increase in revenue and related increase in cost of goods sold resulted in an increase in gross profit of 20.39%.
The increase in general and administrative expenses of 5.29% outpaced the increase revenue, resulting in an increase in operating profit of 31.67%. After deducting the net income, we find that the profit before paying income tax is 47.63% higher than previous year. In 2012 we see there was a net loss at the end of the year, so they got tax shield over that year, means they did not have to give taxes for that year and the following year.
After that, the net worth of the financial assets increased 140.52% over one year, resulting in a large increase of the total comprehensive income of the year by 4376.72%, meaning they have successfully overcome their loss occurred in 2012.
RECOMMENDATION
Summit Power Limited is well-established company. Therefore, it is very tough to recommend on any aspect of the company. However, as it is the requirement of the report so I have come up with few recommendations, after conducting the research.
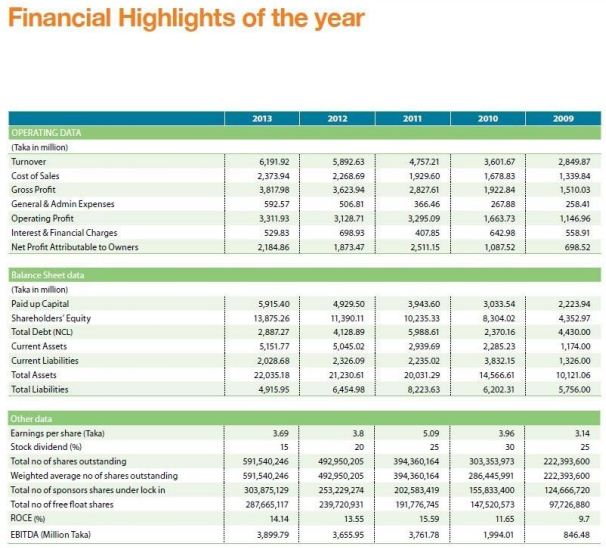
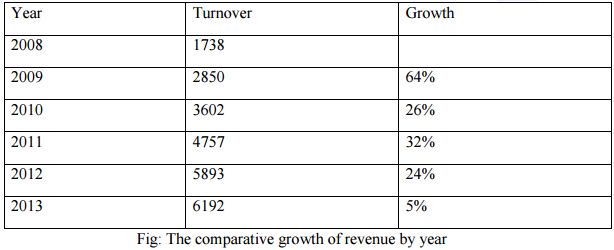
1. From the financial highlights of the company, we can see that the growth of revenue is decreasing comparatively every following year. This shows that the company’s sales are decreasing dramatically over time. In addition to that, growth of gross profit, net profit, total assets, paid-up capital, current asset etc. is decreasing which means that the business is not expanding at all. At this point, in order to expand the business, the company is required to invest in new sustainable projects by increasing its equity and debt financing.
In addition to that, company has already took it’s initiative of increasing its equity financing as there is 21.82% increase of equity in the year 2013 than 2012. At the same time, the company needs to find ways to reduce the cost of sales such as just-in-time delivery of products to reduce the cost of inventory or renegotiating contracts annually with the current suppliers. Almost always these discussions will result in lower cost of goods and increase of profit for the company.
2. From the financial ratio analysis, it is clearly visible that the gross profit margin is showing an increasing trend as the revenue for the company is not increasing that much over the year. Again, company’s sales are not increasing that much compared to the increase of profit. For this reason, company increased their current ratio over time and decreased debt financing or less used the leverage in order to maintain a stronger equity position from any uncertainties. The company is taking less risk by using equity financing. It is high time to reconsider their financing decision as the company is having low P/E ratio which suggests that investors are expecting lower earnings growth in the future. The company can consider debt financing rather than depending on equity financing.
3. From the trend analysis of income statement of Summit ltd., we can see that the company is having a fluctuating trend as in the year 2009, the profit for the company is showing a decreasing trend and again in the year 2011, the profit for the company is showing an increasing trend. The reason behind having a fluctuating trend is that the company has invested heavily in 2010 on Summit’s Narayanganj Plant. The trend of increase of profit lasted in the following years as well as in the year 2013, a large increase of the total comprehensive income by 4376.72%, meaning they have successfully overcome their loss occurred in 2012. This shows a promising future for the company.
CONCLUSION
To conclude, it can be said that it was a lifetime experience for me to work in Summit Power Limited and gather knowledge from here. I have learned so many things practically throughout the entire internship program. I believe all these experience will help me in building a good career in future. All the reputation this company got from a comparatively short lifespan is all because of the discipline, hard work and strategies of the excellent authority they have. In this report, although there were some limitations of obtaining exact internal information but those are carefully taken under consideration so that they do not hamper the results of the research. Last but not the least, it can be said that the ultimate success comes by having great devotion, pledge and dynamic leadership of the management committee and summit will surely walk a long way in the future with their head held high and will continue supplying energy more than ever.