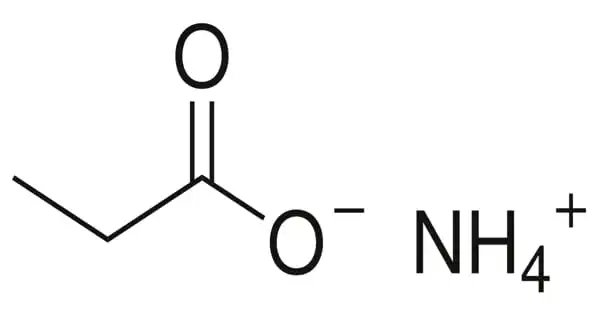
Ammonium propionate, often known as ammonium propanoate, is the ammonium salt of propionic acid. It has the chemical formula NH4(C2H5COO). It is the ammonium salt of propionic acid. It can be utilized as an antiseptic, antifungal agent, preservative, and antimould agent in the food and feed industries.
Ammonium propionate can be used as an antibacterial and antifungal agent. It has antimicrobial effects and produces free propionic acid in acidic environments. It has a specific effect in preventing the synthesis of aflatoxin, but it is practically completely ineffective against yeast. Effective against molds and gram-negative bacilli. The lower the pH, the better the anti-corrosion action.
Properties
It is a colorless crystal in the shape of a column. It has a molecular mass of 91.109. It is soluble in cold water, alcohol, and acetone. It has anticorrosive and fungicidal properties. Propionate ammoniumit exhibits antifungal properties when exposed to acid. The effect is enhanced when the PH value is low. It is low corrosive and volatile when stored below 35°C in a cool, sealed place away from sunshine and water.
- Chemical formula: C3H9NO2
- Molar mass: 91.110 g·mol−1
- Melting point: 45 °C (113 °F; 318 K)
- Boiling point: 141.7 °C (287.1 °F; 414.8 K)
- Solubility in water: 1 g/mL

Reaction
It is created when propionic acid and ammonia combine. It has a slightly unpleasant odor and is yellow or light yellow irregular granular crystals. In ethanol, chloroform, and ether, it is miscible and soluble. It’s both non-toxic and corrosive. It has the potential to cause deliquescence in the air.
Uses
It is found in a variety of items such as fertilizers, water treatment chemicals, and plant protection products. It is also employed in a variety of industries, including industry, forestry, agriculture, and fishing.
It is also used as an antiseptic, antifungal agent, antimould agent, and preservative in the feed and food industries. It is less corrosive and effective against mildew and caking in grains.
Ammonium propionate also reduces aesthetic deterioration by inhibiting bacterial development. Ammonium propionate is the most often used feed and grain preservative in the United States, and the compound of propionic acid and ammonium propionate has the best anti-mildew and bactericidal actions in an acidic environment.