Ammonium Chloride
Definition
Ammonium Chloride (NH4Cl) is a white crystalline compound used in dry cells, as a soldering flux, and as an expectorant. It is obtained as a by-product in different chemical processes, particularly from the Solvay process for production of sodium carbonate from sodium chloride, ammonia, carbon dioxide and water. It is also found around some types of volcanic vents. It is used as a flavoring agent in licorice. Ammonium chloride is the product from the reaction of hydrochloric acid and ammonia.

It is a component of many proprietary cold medicines and cough remedies because of its efficacy as an expectorant, and in veterinary medicine, it is used to prevent urinary stones in goats, cattle, and sheep. It vaporizes without melting at 340 °C (644 °F) to form equal volumes of ammonia and hydrogen chloride. Ammonium chloride is yielded as a by-product in the ammonia-soda process for making sodium carbonate. It also is produced by reaction of ammonium sulfate and sodium chloride solutions.
Application and Uses of Ammonium Chloride
Ammonium chloride is used as a flux in preparing metals to be tin coated, galvanized, or soldered. It is an expectorant in cough medicine and as a systemic acidifying agent in the treatment of severe metabolic alkalosis.
The main application of ammonium chloride is as a nitrogen source in fertilizers (corresponding to 90% of the world production of ammonium chloride) such as chloroammonium phosphate. In 18th century, it was utilized in pyrotechnics, but replaced by safer chemicals. Its function was to provide a chlorine donor to increase the blue and green colors from copper ions in the flame.

In the food industry, ammonium chloride is used as a food additive and yeast nutrient in the making of bread. It is a feed supplement for cattle and an ingredient in nutritive media for yeasts and many microorganisms. It can be found in shampoo, hair color and bleach, body wash and cleanser, facial cleanser, conditioner, hand dishwashing detergent, as well as in bath oils and salts. An important use of ammonium chloride is as electrolyte in dry cell batteries where it is used because it is an ionic compound.
Ammonium chloride is also used in etching in the manufacture of printed circuits, as a fire extinguisher, an explosive in mineral winning and as a curing agent in formaldehyde-based adhesives.
It is used as a diuretic for people with edema or Läennex diseases. A dose of nine grams per day is recommended. Ammonium chloride acts by increasing the renal excretion of chloride. At the same time, also used as an acidifier, as this salt result in increased acidity concentrations of free hydrogen ions. It is used as a systemic acidifying agent in treatment of severe metabolic alkalosis, in oral acid loading test to diagnose distal renal tubular acidosis, to maintain the urine at an acid pH in the treatment of some urinary-tract disorders.
Ammonium chloride is used in the textile and leather industry, in dyeing, tanning, textile printing and cotton clustering. Around the turn of the 20th Century, Ammonium Chloride was used in aqueous solution as the electrolyte in Leclanché cells. These cells found a commercial use as the “local battery” in subscribers’ telephone installations.
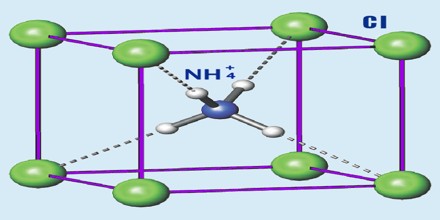
Sublimated ammonium chloride can be found in cavities in the earth close to volcanoes. The salt can be manufactured industrially directly from ammonia and hydrochloric acid, but that is often not the most favorable method from an economic point of view. Ammonium chloride is obtained as a by-product in different chemical processes, particularly from the Solvay process for production of sodium carbonate from sodium chloride, ammonia, carbon dioxide and water.