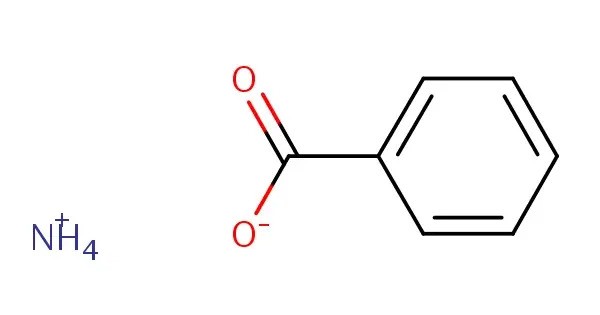
Ammonium benzoate, a white powder-like substance, is the ammonium salt of benzoic acid. It is the ammonium salt of benzoic acid. It’s commonly used as a preservative and an intermediate in organic synthesis. This compound is prepared by the reaction of benzoic acid and ammonia.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C7H9NO2
- Molar mass|: 139.15 g/mol
- Appearance: White solid
- Density: 1.26 g/cm3
- Melting point: 198 °C (388 °F; 471 K)
- Solubility in water: 21.3 g/100 mL (20 °C), 83 g/100 mL (100 °C)
- Solubility: soluble in methanol, insoluble in diethyl ether
- Odor: Odorless or slight ammonia smell
- pH (1% solution): ~7–8
- Stability: Stable under normal conditions
- Decomposition: Releases ammonia and benzoic acid
Reactions
Ammonium benzoate can be dehydrated to form benzamide.
Preparation
Ammonium benzoate is typically prepared by neutralizing benzoic acid with ammonia (NH₃):
C₆H₅COOH (benzoic acid) + NH₃ → C₆H₅COONH₄ (ammonium benzoate)
Chemical Behavior
Forms from the neutralization of benzoic acid with ammonia:
C6H5COOH + NH3 → C6H5COONH4
In aqueous solution, it can revert to ammonia and benzoic acid depending on pH.
Occurrence and Applications
Industrial Uses:
Preservative agent: Though less common than sodium or potassium benzoate.
- Intermediate in chemical synthesis.
- Corrosion inhibitor in antifreeze or cooling systems.
- Plastic additive for modifying polymer properties.
Biological and Environmental Presence:
- Not naturally occurring in large quantities.
- Can be formed in lab or during processing of benzoic acid with ammonia.
- It is biodegradable, and under microbial action, it breaks down into simpler compounds.
Safety and Handling
- Low toxicity in small quantities.
- Irritant: Can cause mild skin and eye irritation.
- Decomposes on heating to release irritating fumes (ammonia and benzoic acid).
- Use gloves and eye protection when handling in bulk.