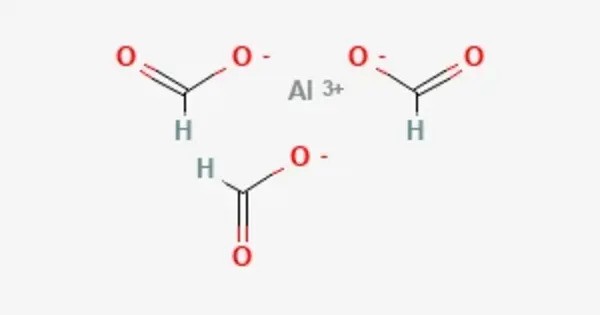
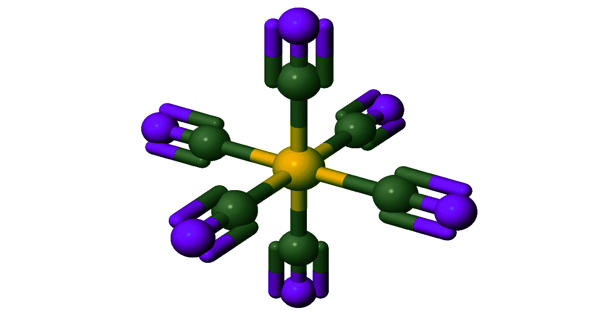
Aluminium formate is the aluminium salt of formic acid, with the chemical formula Al(HCOO)3. It can be produced via the reaction of aluminium soaps and formic acid. It exists in various forms, often as a white, crystalline substance. The aluminium ion (Al³⁺) is coordinated to three formate ions (CHO2⁻), forming a coordination complex.
Reaction between formic acid and aluminium hydroxide yields Al(HCOO)3(CO2)0.75(H2O)0.25(HCOOH)0.25. Upon activation at 180 °C, guest molecules are removed to obtain Al(HCOO)3.
Properties
Aluminium formate is thermally unstable and can decompose when heated, often leading to the formation of aluminium oxide (Al2O3), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water. It can react with bases to form aluminium hydroxide and with acids to release formic acid. It is typically hygroscopic, meaning it can absorb moisture from the air.
Chemical formula: C3H3AlO6
Molar mass: 162.033 g·mol−1
Appearance: White powder
Solubility in water: Insoluble
Synthesis
Aluminium formate is generally synthesized in the laboratory through the reaction of aluminium salts (such as aluminium chloride) with formic acid or its derivatives. It is not typically found naturally in significant amounts in the Earth’s crust, but could theoretically be produced in environments rich in both aluminium and formic acid.
Applications
Due to its properties, aluminium formate is occasionally used in materials science, as a precursor in the synthesis of other aluminium compounds, and for use in certain types of catalysts or chemical reactions.