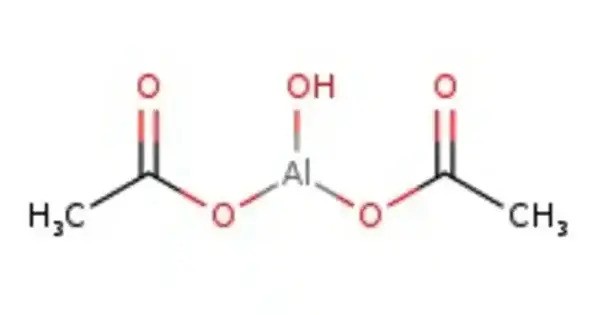
Aluminium acetate or aluminium ethanoate (also “aluminum ~”), sometimes abbreviated AlAc in geochemistry, can refer to a number of different salts of aluminium with acetic acid. It is a chemical compound typically used in medicine, cosmetics, and industrial applications.
In the solid state, three salts exist under this name: basic aluminium monoacetate, (HO)2AlCH3CO2, basic aluminium diacetate, HOAl(CH3CO2)2, and neutral aluminium triacetate, Al(CH3CO2)3. In aqueous solution, aluminium triacetate hydrolyses to form a mixture of the other two, and all solutions of all three can be referred to as “aluminium acetate” as the species formed co-exist and inter-convert in chemical equilibrium.
Properties:
- White, water-soluble solid (in solution forms).
- Mildly acidic due to acetic acid component.
- Acts as an astringent (shrinks body tissues), antiseptic, and anti-inflammatory.
- Appearance: White powder or granular solid
- Solubility: Soluble in water (forms acidic solution)
- Odor: Slight vinegar-like (from acetate group)
- Density: ~1.5–1.6 g/cm³ (varies with composition)
- Melting Point: Decomposes before melting
- pH (aqueous solution): Acidic to neutral depending on form
Preparation
Typically prepared by
- Reacting aluminium hydroxide or aluminium sulfate with acetic acid or sodium acetate.
- Industrially, prepared using a double decomposition process involving aluminium salts and acetates.
Uses
- Medical (topical): As an astringent, antiseptic, and anti-inflammatory in skin conditions (e.g., in Burow’s solution).
- Textiles: As a mordant in dyeing processes.
- Analytical chemistry: For precipitation or buffering.
- Veterinary use: To treat infections and irritation.
Natural Occurrence
- Does not occur naturally in pure form.
- May be present in trace amounts where organic matter and aluminium minerals interact in acidic environments (e.g., soils or decomposing leaf litter).
- Mostly synthetically produced for commercial and pharmaceutical use.