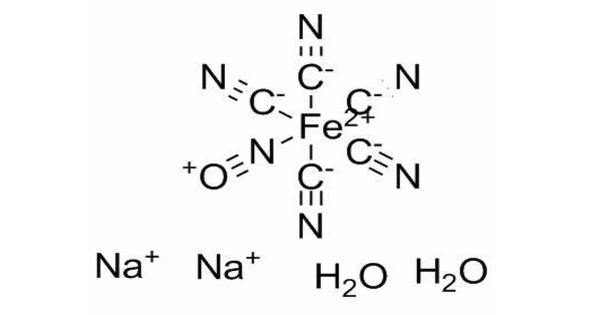
Sodium nitroprusside (SNP), sold under the brand names Nitropress and others, is a blood pressure medicine. It is a prescription medicine used to treat high blood pressure. This may be done if the blood pressure is excessively high and causing symptoms, in certain types of heart failure, and after surgery to reduce bleeding. It is administered by continuous injection into a vein.
It is a vasodilator, which means it relaxes and dilates the blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more freely. This impact lessens the workload on the heart and may aid in blood pressure reduction. The effects are practically immediate and might last up to ten minutes. It is also available as a generic drug.
Here are some key points about sodium nitroprusside:
- Mechanism of Action: It works by releasing nitric oxide (NO) in the bloodstream, which causes relaxation of smooth muscle in blood vessels. This leads to vasodilation and a decrease in blood pressure.
- Medical Uses: It is typically used in situations where blood pressure needs to be lowered quickly, such as during hypertensive emergencies, congestive heart failure, or during surgery.
- Administration: It is usually administered as an intravenous infusion under close medical supervision, as it acts rapidly and its effects can be adjusted as needed.
Side Effects
Common side effects may include headache, nausea, vomiting, and a rapid drop in blood pressure. In excessive doses or with prolonged use, it can lead to cyanide toxicity, which is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition.
Due to the risk of cyanide toxicity, sodium nitroprusside is only used in a hospital or clinical setting, and its use is closely monitored.
Cyanide Poisoning
To mitigate the risk of cyanide toxicity, sodium nitroprusside is typically administered with sodium thiosulfate, which helps convert cyanide to a less toxic compound that can be eliminated by the body.
Side effects and mechanism
Low blood pressure and cyanide poisoning are common adverse effects. Methemoglobinemia is another major negative effect. Because of the risk of side effects, it is not generally suggested during pregnancy. High doses should not be taken for more than 10 minutes. It works by boosting nitric oxide levels in the blood, which raises cGMP levels in cells and produces blood vessel dilatation.