Alum-(K) is a hydrous potassium aluminum sulfate mineral with formula KAl(SO4)2·12(H2O). It is the mineral form of potassium alum and is referred to as potassium alum in older sources. It is a member of the alum group.
Occurrences include Mount Vesuvius, Italy and Alum Cave, Sevier County, Tennessee.
General Information:
- Category: Sulfate mineral
- Formula: KAl(SO4)212(H2O)
- Crystal system: Cubic
- Member of: Alum Group
- Density: 1.757 g/cm3 (Measured) and 1.753 g/cm3 (Calculated)
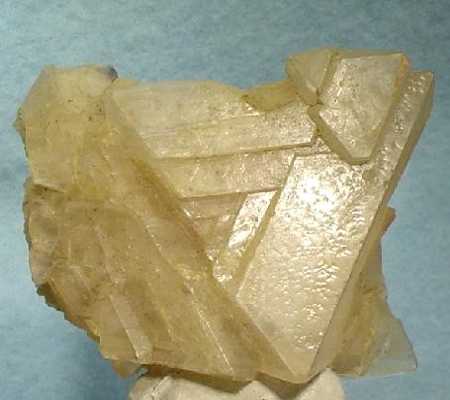

Properties
- Color: Colorless, white
- Crystal habit: Stalactitic, columnar, granular, massive efflorescences; rare as small octahedral crystals
- Fracture: Conchoidal
- Mohs scale hardness: 2-2.5
- Luster: Vitreous
- Diaphaneity: Transparent
- Specific gravity: 1.757
- Optical properties: Isotropic
- Transparency: Transparent
Occurrence
It occurs as colorless to white, soft isometric crystals and efflorescence coatings. Rare crystals are octahedral in form if occurring as precipitates from neutral water solution, but cubic in form if the solution is alkaline.
It occurs as a precipitate around volcanic fumaroles and solfataras. It also occurs as an alteration in argillaceous sediments or coal beds which contain oxidizing sulfide minerals (pyrite or marcasite). Occurs associated with alunogen, pickeringite, epsomite, melanterite, gypsum and native sulfur.
Information Source;