Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is essentially a telephone connection over the Internet, also known as IP telephony. It is a system and a collection of technologies for the provision of voice communications and multimedia sessions over networks of the Internet Protocol (IP), such as the Internet. Some VoIP administrations permit clients to call individuals utilizing similar assistance, however, others may permit clients to call anybody. The information is sent carefully, utilizing the Internet Protocol (IP) rather than simple phone lines.
Some VoIP services run only on a user’s device or a special VoIP phone, while other services allow them to use a standard VoIP adapter-connected phone. This enables individuals without having to pay long-distance or international phone rates to speak to each other long-distance and across the globe. The terms Internet telephony, broadband telephony, and mobile telephony refer explicitly to the provision by the public Internet of communications services (voice, fax, SMS, voice-messaging) rather than the public switched telephone network (PSTN), sometimes referred to as plain old telephone service (POTS).

Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
By making existing phone lines and networks almost redundant and reducing demand for them dramatically, VoIP changed the telecommunications industry. Voices are converted by VoIP services which travel over the Internet into a digital signal. The signal is converted to a standard telephone signal, i.e. an analog signal if a normal telephone number is called before it reaches its destination. A consumer requires a computer, an Internet connection, and VoIP software in order to use VoIP. A microphone, analog telephone adapter, or VoIP phone are also necessary for a consumer. In locations such as airports, hospitals, cafes, etc., wireless hot spots allow users to connect to the Internet and can wirelessly use VoIP services.
For telecommunications providers, it is increasingly common to use VoIP telephony as a backhaul over dedicated and public IP networks to link switching centers and to interconnect with other providers of telephony networks; this is also referred to as IP backhaul. Another choice which connects directly to a router through Ethernet or wirelessly is IP phones. These phones have all the requisite VoIP apps built-in and do not need a computer as a result. VoIP phones plug directly into the broadband link of users and work largely like a conventional phone. If a phone with a VoIP adapter is used by consumers, they can dial just as they always have, and a dial tone can also be given by the service provider.
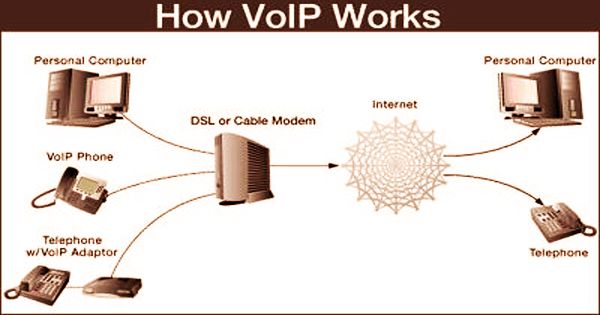
How voice over internet protocol (VoIP) works
The benefits of VoIP technology are that the expense of voice communication for personal and commercial use is reduced to almost zero. As an opportunity to purchase broadband or higher speed Internet access and Internet cable television networks, many Internet providers throw in VoIP telephone service free of charge for personal subscribers. Business-oriented VoIP solutions have developed into centralized communications systems that treat all telephone calls, faxes, voice mail, e-mail, web conferences, and more as distinct units that can all be distributed by any means and to any mobile device, including mobile phones.
During power outages, some VoIP services don’t function and the service provider does not provide backup power. The broader market has increasingly moved towards ‘Internet’ or Hosted ‘VoIP solutions, though many use cases still exist for private or on-site VoIP systems. Not all VoIP systems, via emergency service numbers, link directly to emergency services. Providers of VoIP may or may not provide directory assistance, too.
Information Sources: