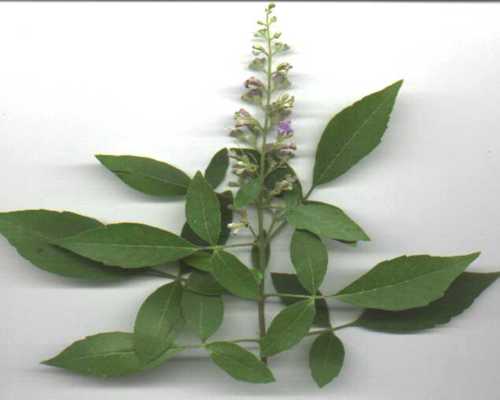
Vitex Peduncularis Plant
Vitex is a genus of about 250 species of shrubs and trees from 1-35 m tall, native to tropical, subtropical and also warm temperature regions throughout the world. In the past widely included in the family Verbenaceae, it has recently been transferred to the family Lamiaceae (Labiatae).
- Botanical name: Vitex peduncularis
- Division: magnoliophyta
- Class: magnoliopsida
- Order: lamiates
- Family: lamiaceae(labiatae)
- Genus: vitex
Description
Vitex peduncularis is a big sized tree of Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Nepal, Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam. The trees are 5-15 m tall. Branchlets, sparsely pubescent when young, glabrescent. Leaves 3-foliolate; petiole 4-7 cm; petiolules 5-12 mm; leaflets broadly canceolate to oblong, glabrous, abaxially densely glandular, base cuneate and slightly oblique, margin entire or slightly undulate and ciliate, apex acuminate to acute; central leaflet 10-15 4-5cm. Thyrses 7-17cm; bracts linear, early deciduous. Calyx 1•8-2•5 cm, outside pubescent and glandular, inside glabrous. Corolla white, outside pubescent, lower lip pilose inside. Stamens included; filaments glabrous. Overy glabrous. Fruiting calyx minutely 5-dentate to subtruncate. Fruits black, subglobose, ca. 7mm in diam., with longitudinal veins when dry.

Medicinal importance of Vitex peduncularis
The plant is used in various ways, chiefly as an infusion of the leaves or of the root bark or young stem bark, in fever of malarial type, and especially in blackwater fever (Kirtikar et. al., 1987). Several cases of malarial fever and black water fever were successfully treated with the infusion of the leaves(J.C.S. Vaughan, 1921).
The bark is also used for making an external application for pains in the chaste.
In series of cases malarial fever, however, caused by Plasmodium vivex, P. malariae and Laveraniae malariae, the freshly prepared infusion of dried leaves had no effect whatever on the parasites in the blood, on the temperature chart or on the other clinical symptoms. The drug appears to be absolutely useless in the treatment of malaria (Chopra et.al., 1924).
Reported biological investigation on Vitex peduncularis
Suksamrarn et al, 2004, reported butanol ext. of Vitex peduncularis exhibited anti-inflammatory activity. Pedunculariside, together with the known iridoid agnuside isolated from the butanol ext. of Vitex peduncularis stem bark. Both pedunculariside and agnuside showed preferential inhibition of COX-2, with IC50 values of 0•15±0•21 mg/mL and 0•026±0•015mg/mL respectively, while having only small inhibitory effects on COX-1, Both compounds do not exhibit cytotoxicity against vero cells.
Information Source;