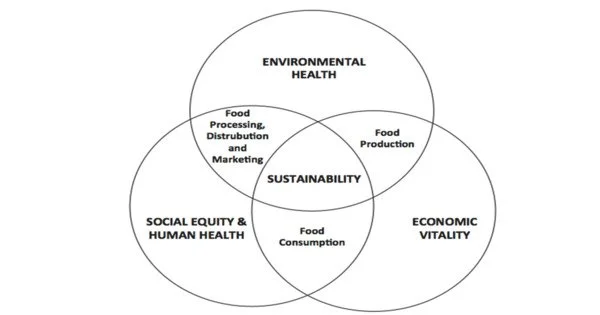
A sustainable food system is a form of food system that offers healthful food to people while also creating environmentally, economically, and socially sustainable food systems. It refers to a system that delivers healthy food to meet current food requirements while also preserving ecosystem health and the ability to supply for future generations. It includes several aspects of food production, distribution, consumption, and waste management.
Sustainable food systems begin with the development of more sustainable agriculture techniques, followed by the development of more sustainable food distribution systems, the development of sustainable diets, and the decrease of food waste throughout the system. Developing a sustainable food system is critical for addressing environmental, social, and economic issues related to food production and consumption. Many or all of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals have been claimed to be dependent on sustainable food systems.
Here are the key elements and principles of a sustainable food system:
Environmental Stewardship:
- Regenerative Agriculture: Promoting farming practices that enhance soil health, reduce chemical inputs, and increase biodiversity.
- Water Conservation: Efficient water use and reduction of water pollution in agriculture.
- Reduced Emissions: Minimizing greenhouse gas emissions associated with food production and transportation.
Local and Regional Food Systems:
- Supporting Local Producers: Encouraging consumers to buy locally grown and produced food to reduce transportation emissions and support local economies.
- Shorter Supply Chains: Reducing the distance food travels from farm to plate, which decreases energy use and food waste.
Healthy Diets:
- Nutrition Education: Promoting balanced and healthy diets to reduce diet-related health problems.
- Reducing Food Waste: Minimizing the amount of edible food that goes to waste in the production and consumption process.
Social Equity:
- Fair Wages: Ensuring that all workers in the food system, from farmers to restaurant staff, receive fair compensation and safe working conditions.
- Access to Food: Ensuring that all communities have access to affordable, nutritious food, addressing issues of food deserts and food insecurity.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health:
- Preserving Ecosystems: Protecting natural habitats and biodiversity through sustainable land use practices.
- Reducing Pesticide Use: Minimizing the use of harmful chemicals that can harm non-target species.
Moving to sustainable food systems, including moving consumption to sustainable diets, is a critical component of tackling the causes and reacting to climate change. According to a 2020 analysis prepared for the European Union, the food system, comprising agricultural and livestock production, transportation, changing land use (including deforestation), and food loss and waste, can account for up to 37% of global greenhouse gas emissions. One key component of this transformation is the reduction of meat production, which accounts for ~60% of greenhouse gas emissions and ~75% of agriculturally used land.