Strategic Programs (STRAP) for 2012-2013 of Airtel Bangladesh
Airtel Bangladesh Ltd. is a GSM-based cellular operator in Bangladesh. Airtel is the sixth mobile phone carrier to enter the Bangladesh market, and originally launched commercial operations under the brand name “Warid Telecom” on May 10, 2007. Warid Telecom International LLC, an Abu Dhabi based consortium, sold a majority 70% stake in the company to India’s Bharti Airtel Limited for US$300 million. Bharti Airtel Limited took management control of the company and its board, and rebranded the company’s services under its own airtel brand from December 20, 2010. The Bangladesh Telecommunication Regulatory Commission approved the deal on Jan 4, 2010. Bharti Airtel made a fresh investment of USD 300 million to rapidly expand the operations of Warid Telecom and have management and board control of the company. This is the largest investment in Bangladesh by an Indian company. Dhabi Group continues as a strategic partner retaining 30% shareholding and has its nominees on the Board of the Company.
The new funding is being utilized for expansion of the network, both for coverage, capacity, and introduction of innovative products and services. As a result of this additional investment, the overall investment in the company will be in the region of USD 1 billion.
This is Bharti Airtel’s second operation outside of India. The company launched its mobile services in Sri Lanka in January 2009 on a state-of-the-art 3.5G network. On July 19, 2007, the company crossed the 1 million customers mark in the first 70 days of operation. Airtel Bangladesh had 6.345 million subscribers as of March 2012. Bharti Airtel Limited operates in 20 countries across South Asia, Africa and the Channel Islands. It operates a GSM network in all countries, providing 2G, 3G and 4G services depending upon the country of operation. Airtel is the third largest telecom operator in the world with over 243.336 million customers across 20 countries as of March 2012. It is the largest cellular service provider in India, with over 181 million subscribers at the end of March 2012.
History
In December 2005, Warid Telecom International LLC paid US$ 50 million to obtain a GSM license from the BTRC and became the sixth mobile phone operator in Bangladesh. In a press conference on August 17, 2006, Warid announced that its network would be activated two months ahead of schedule, in October, 2006. Again in October, 2006 Warid Telecom put off the launch of its cell phone services in Bangladesh until April, 2007 after its major supplier Nokia walked out on an agreement over a payment dispute. Warid had a soft launch at the end of January 2007. It gave away complimentary subscriptions among a selected group of individuals, whose job was to make ‘test calls’ and the operator adjusted its network’s quality based on their comments. On June 10, 2008, Warid Telecom expanded its network to 3 more districts Bandarban, Khagrachhari and Rangamati. Now all 64 districts of Bangladesh are under Warid network coverage meaning Warid Telecom now has nationwide coverage. On December 20, 2010, Warid Telecom was rebranded to airtel.
On December 21, 2011, Airtel Bangladesh launched “Airtel Circle of Friends”, the first ever Interactive Commercial in Bangladesh, created and executed by Digimarka. Sunil Bharti Mittal founded the Bharti Group. In 1983, Mittal was in an agreement with Germany’s Siemens to manufacture push-button telephone models for the Indian market. In 1986, Mittal incorporated Bharti Telecom Limited (BTL), and his company became the first in India to offer push-button telephones, establishing the basis of Bharti Enterprises. By the early 1990s, Sunil Mittal had also launched the country’s first fax machines and its first cordless telephones. In 1992, Mittal won a bid to build a cellular phone network in Delhi. In 1995, Mittal incorporated the cellular operations as Bharti Tele-Ventures and launched service in Delhi. In 1996, cellular service was extended to Himachal Pradesh. In 1999, Bharti Enterprises acquired control of JT Holdings, and extended cellular operations to Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh. In 2000, Bharti acquired control of Skycell Communications, in Chennai. In 2001, the company acquired control of Spice Cell in Calcutta. Bharti Enterprises went public in 2002, and the company was listed on Bombay Stock Exchange and National Stock Exchange of India. In 2003, the cellular phone operations were rebranded under the single Airtel brand. In 2004, Bharti acquired control of Hexacom and entered Rajasthan. In 2005, Bharti extended its network to Andaman and Nicobar. This expansion allowed it to offer voice services all across India. In 2009, Airtel launched its first international mobile network in Sri Lanka.Today, Airtel is the largest cellular service provider in India and the fourth largest in the world.
Purpose & Function of OE
The department I worked in as an intern is “Operational Excellence” in short it is called “OE” in Airtel. This department currently consists of four officials including the head of the department Zakia Sultana who is a member of Airtel leadership board (ALB) & has experience in the telecom industry for more than 12 years. The other officials are Md. Ahmadul Haque (Process management manager), Jinat Laila (Process manager commercial) & Shanjida Rahman (Process improvement manger).
In the online business dictionary the term operational excellence is described as “A philosophy of the workplace where problem-solving, teamwork, and leadership results in the ongoing improvement in an organization. The process involves focusing on the customers’ needs, keeping the employees positive and empowered, and continually improving the current activities in the workplace.”
This organizational philosophy is clarified in “Wikipedia” a bit more by describing “Much of this philosophy is based on earlier continuous improvement methodologies, such as Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, and Scientific Management. The focus of Operational Excellence goes beyond the traditional event-based model of improvement toward a long-term change in organizational culture.”
Bharti Airtel established its own “Operational excellence model & policy” during 2009-2010 & since then they follow that model accordingly. The Operational excellence policy of Bharti Airtelis is expressed by the following statement which is “Delivering best value to our customers & stakeholders with zero waste & zero variation.” Their objective is to achieve these through continuous improvement & making the process by being
- Faster (Access)
- Better (Utility)
- Cheaper (Cost)
- Easier (Hassle Free)
The principle business activities of Airtel that is done through “Operational Excellence” are followings:
- Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
- Value Stream Mapping
- Performance Variance reduction (PVR)
- Knowledge Management (KM)
- Process Management.
- Training & Certification. ( Six Sigma training & other OE tool trainings excluding HR parts.)
- Compliance ( Here TL9000 is followed which is a Quality Management System designed specifically for the Telecommunications Industry. It is based around ISO 9000 and was developed by the Quality Excellence for Suppliers of Telecommunications (QUEST) leadership forum in response to product and service failures within the industry.)
- Measurement & Research.
The expectations of the Airtel board of directors towards OE as well as their its main focus are followings.
- Scientific Thinking
- Cross function working
- Structured problem solving
- Process document, standardization & compliance
- Waste & variation reduction
- Making quality “A way of Life” for Airtel.
The scientific thinking & structured problem solving involve all the OE tools that is used for defining, measuring, analyzing, improving & controlling of all the process that is undertaken by the company. The “Six Sigma” quality management philosophy is the heart & soul of OE functions for all of these activities.
Here, cross functional participation of all the departments of Airtel is a must & that is how the annual strategic plans are fulfilled. Additionally, knowledge management also play a vital role by spreading the internal & external “best practice” news to each & every functions. In order to do the value stream mapping they adopt “Microsoft Visio” software through which they give all the function & process a clear visibility to the owner of the process so that the owners of the process can clearly understand the flow of work & act accordingly. Overall, the purpose of all of these activities is to reduce the performance variation of each & every departments, increase the performance standards of each of the segments & thus enhancing the quality of organizational performance of Airtel.
As mentioned earlier that for the process management, improvement, documenting, standardizing & lastly for the measurement of performance , the “Six Sigma” scientific management procedure is adopted which is the heart & soul of OE. The head of OE, Zakia Sultana herself is the only certified master black belt of this method in Airtel Bangladesh. According to Wikipedia the “Six Sigma is a set of tools and strategies for process improvement originally developed by Motorola in 1985. Six Sigma seeks to improve the quality of process outputs by identifying and removing the causes of defects (errors) and minimizing variability in manufacturing and business processes. It uses a set of quality management methods, including statistical methods, and creates a special infrastructure of people within the organization (“Champions”, “Black Belts”, “Green Belts”, “Orange Belts”, etc.) who are experts in these very complex methods.”
Six sigma method focuses on quality way more intensely then the classical 3.8 sigma method which sates 99% good quality where in six sigma it is 99.99% good quality. For a business, the Sigma Capability (Zvalue) is a metric that indicates how well the process is performing. Here, when the defects goes down, the sigma capability (Z-value) goes up. This is the very basic of the measurement process.
In Airtel, the core of this method is the DMAIC approach. This approach is adopted in the following way,
- Define- Identify a manageable, customer focused problem area for improvement. (Practical problem)
- Measure- Understand the measures around the problem, the measurement system & create a baseline. (Statistical problem)
- Analyze- Identify the variable(X) which have the maximum impact on the problem (Y). (Statistical solution)
- Improve- Implement the solution. (Practical solution).
- Control- Sustain the results.
In the “Define” phase two things are given importance, one is the voice of customer (VOC) & the critical to quality (CTQ) factor. Usually the market research that is done by OE brings forth the voice of customers & from that they sort out the improvable pain points. Then they convert VOC in to measurable CTQ’s.
In the “Measure” phase four things are taken care of, firstly basic statistics, secondly establishing performance standards, thirdly measurement system analysis & lastly capability analysis. In the “Analyze” phase the statistical tools are used such as box plot, scatter plot, correlation, regression etc. Before that to identify the variable “X” which has impacts on problem “Y” they adopt brainstorming, process mapping, pareto analysis, fish bone methods.
In the “Improve” phase the action plan is presented in detail where each process owner is clearly showed their problems, causes, proposed solutions(targets), responsibility & timeline.
In the “Control” phase there involves quality planning, mistake proofing, control charts, statistical process controls & project closures. Each year at every AOP ( Annual Operational Plan) session of Airtel, the OE is given new strategic programs from the strategy makers & then those programs are given a cross functional shape to distribute the responsibility of each & every programs of that year. Usually the chief leader of each programs are called “Sponsor” & they are usually the members of ALB. At each AOP session the results of the previous programs are also disclosed through OE head & winners are rewarded by the C.E.O.
Project Summery
Strategic programs are a regular practice of Airtel Bangladesh since its inception. Every year the board of directors, CEO along with the Airtel leadership board members set up the strategic objectives of those years & according to that they prepare the strategic plans for the year. Keeping aligned with those strategic plans they establish several strategic programs for that year which are known as “STRAP” at Airtel. These STRAPs are disclosed during the AOP session of Airtel. Each of this STRAP has distinct objectives & goals to achieve & are formulated in such a way where each STRAP requires to have at least one ALB member as chief leader who are called “Sponsor” of the STRAP. Under each STRAP there are several projects & for each of those projects at least one project leaders are assigned. Rest of the officials that work in each STRAP are called “team members”. One of the major characteristics of these STRAPs is that it always involves cross-functional participation of the members without which the objectives can never be achieved.
OE bears the sole responsibility to measure the performance of each of these STRAP in every quarter of a year. “Master Black belt” for each of the STRAP is OE head where the rest of the OE officials are certified process “Black belts” & they assist their respective assigned STRAPs & calculate the performance of those programs. In this way at the end of the year the most successful program that achieved its objective in the most efficient manner are found & the whole team is rewarded by the CEO through “CEO Trophy” at the AOP session.
The number of strategic programs for the last annual year 2012-1013 was eight. Each of these STRAP had different objectives & action plans. As I was assigned to prepare a video presentation about these eight STARPs activities by OE head Zakia Sultana, I had to go through the objectives of this STRAPs in order to have an insight about each of the programs & relate those visually in the video creation. The purpose of this video was to create a visual entertainment regarding the previous year’s STRAP activities in the AOP session where the winner is declared.
Objective of the report: The objective of this report is to discuss briefly about the 2012-2013 annual strategic programs of Airtel through which we will have a depth knowledge on how these TELCO design & implement its strategic objectives in order to compete in this highly competitive industry.
Methodology
Primary data: The primary data of this report is taken from the power point slides that is stored in the OE drives in their computer. From that all the STRAP related info are gathered to have an understanding of these programs.
Secondary data: This is a bit exploratory in kind as the secondary data for this report is taken from the OE officials who clarified the complex issues to me & enhanced my understanding through verbal question answer communication.
Name & Objectives of the Eight STRAPs for 2012-2013
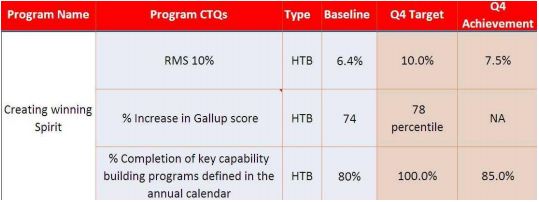
Creating Winning Spirit
Business Case: Airtel BD being the 4th largest operator is in a challenger position in Bangladesh. Airtel have very high ambition to grow: much faster than market and beat the competition. To do it Airtel need a team who believes in winning. There is a general feeling that we lack the winning spirit. Besides, comparing our Gallup score (which is an employee engagement process where employees are to fill up questionnaires set by HR) on employee engagement (67 percentile) with BL or best performing companies, Airtel have good degree of improvement scope.
Objective of the STRAP: Create and Enhance the Winning Spirit in Airtel Bangladesh Employees.
STRAP Outline
Sponsor of the Program: ALB member Noor Mohammad who is the functional head of Human Resources department.
Black Belt of the Program: Shanjida Rahman, Process Improvement Manager, OE. There were three projects under this program,
- Engage to create Winning Spirit : The aim of this project was to create engagement to bring out the winning spirit in the employees. The name of the project leader is Asif Ahmed. The key CTQ’s ( Critical to quality) for this project was to increase the score of winning spirit survey & to increase the gallup score. The key action plans that were taken under this project included giving employees general company direction, expectation & business updates, creating employee newsletters, giving people manager award, open house session with CXO’s, creating family day, arranging airtel night, arranging team & functional activity workshop, Providing RMS info to all employee , creating communication on suggestion & complain box in every facility, arranging focus group discussion with selective groups.
- Improve Quality of Performance Management: The aim of this project was to have one-onone performance feedback. The name of the project leader is Saiful Islam. The key CTQ’s for this project was to enhance the percentage completion of one-on-one performance feedback actions. The key action plans that were taken under this project included creating segment strategies for talent growth & retention, talent segmentation, induction framework for new hire & creating a hiring mix.
- Capability Building: The aim of this project was to have right person in right job & enhancing their capability. The name of the project leader is Nayeem Anam. The key CTQ’s for this project was to enhance the percentage completion of key capability building programs defined in the annual calendar. The key action plans that were taken under this project included creating frontline capability program for sales, marketing & customer service, providing leadership training, creating ZBM capability program, providing coaching (Top to bottom within function), mentoring.
The quarter four performance of this program measured by OE is like the diagram given next.
TROY (Chittagong turn around)
Business Case: Chittagong has a quite good GDP contribution in the overall GDP of Bangladesh but Airtel’s revenue contribution from Ctg is only 14%, while their closest competitor Robi gets 60% revenue contribution from this port city Ctg.
Objective of the STRAP: To increase Airtel’s Ctg revenue up to 35% by the end of the year. Destabilize Robi’s foot hold in Ctg, resulting is loss of their market share & gain for Airtel.
Sponsor of the Program : ALB member Raghvendra Gupta.
Black Belt of the Program: Md. Ahmadul Haque, Process Management Manager, OE.
STRAP Outline
So, there were three projects under this program,
- WAR (Winning Across Revenue): The aim of this project was to have + market share than Robi which means if Robi have “X” customers there Airtel want “X+1” customer & also to have 2% RMS growth in every quarter. The name of the project leader is Rabiul Alam. The key CTQ’s was to beat Robi in terms of RMS & SIM selling units. The key action plans that were taken under this project included setting up targets by sharing format with team & ZBM, finalizing the format and Set the target distribution wise, creating weekly update on distributors performance & reporting Thana wise weekly tertiary status according to the report format.
- Trojan (Killing Robi): The aim of this project was to be the 2nd best of SOP (Share of Preference) by quarter 2 & to have minimum two strategic hits in each quarter. The name of the project leader is Soumen Mittra. The key CTQ’s were to enhance the share of preference drastically & to get two strategic hits for enhancing Airtel’s brand perception at Chittagong. The key action plans that were taken under this project included revamping the distribution of Airtel in Chittagong by appointing 16 new distributors, training them properly, appointing 65 new field service executives (FSE), increasing notice ability of the brand & increasing retailers recommendations.
- Helen (Engaging team to win over competition): The aim of this project was to have most engaged and energetic team & to create Gold platted coverage in urban and outskirts areas of Chittagong. The names of the three project leaders are Saiful Islam, Mamun-Ar-Rashid, Anupom Kumar. The key CTQ’s were to successfully enhance the engagement between the team members & to establish the gold platted coverage in the urban & outskirts areas. The key action plans that were taken under this project included TM ( Trade Marketing) training, Team Building Outing, Sales Manager Training, ZBM Training , Gallup Meeting , Skip Level Meeting, Reward & Recognition.
Mission Outclass ( Turning around zonal gross addition & revenue):
Business Case: At present at most Thana’s, in comparison with competitors Airtel is either in the 2nd to 4th position in most of the zones in terms of revenue and gross additions made each month.
Even though many sites have come up in the past one year, it was not bringing significant revenue back to the company, and were falling under the LRLU( Low revenue low utilization) category further enhancing Airtel’s annual OPEX cost.
Objective of the STRAP: The main aim of this program is to quickly turn around the company in all zones and increase revenue by 20-30% in all zones. By quarter four to enhance the percentage of RMS & SOGA ( Share of gross add) at each of the five zones considered, increasing Thana wise LSO (Load selling unit)/SSO & enhancing BTS utilization, also creating retailers engagement.
Sponsor of the Program: ALB member S K Mukhopadhyay who is the CFO of Airtel BD.
STRAP Outline
So, there were three projects under this program,
- Trade Delight: The aim of this project was to revamp the distribution channels of the zones by engaging the retailers & distributors, thus enhancing the TOMA,REI & SOGA score. The name of the project leader is Mahboob Hossain. The key CTQ was to create delight to person / organization in the channel who will be participating in all event of Airtel. The key action plan that were taken under this project included merging the big area based Thana under several TM (Territory Manager) so that those areas distribution can be served properly, running “Airtel Mela” function at the bazaar places of different rural Thana in order to enhance SIM selling & rural branding & the security of the BTS site enhanced where necessary. Realistic monthly sales target were given as per market scenario and strictly monitored required daily/weekly basis & Thana wise distributor’s ROI (Return On Investment) were set.
- Know Your Network: The aim of this project was to enhance the knowledge level of channel partners regarding Airtel’s network. More precisely, it is the retailers & distributors who play the frontline role for introducing a brand’s network perception to the customer. So, if they are informed properly about Airtel’s network development then they can pass on the news to the customer. In this way they wanted to increase the zonal revenue & decrease LRLU sites. In order to do so it was the Engineering department’s responsibility to share the BTS performance information to the other functions. The name of the project leader is Fayaz Ahmed. The key CTQ was to enhance Thana wise knowledge level of the all the stakeholders regarding zonal BTS performance. The key action plan that were taken under this project included to count the present BTS at every zones also to count the BTS number of other operators, preparing questionnaire for doing survey on network knowledge & perception.
- Compass: The aim of this project was to enhance the SOP & TOMA score of Airtel at the priority zones. Market visibility & retailers recommendation was the prime concern for this project. The name of the project leader is Moshiur Rahman. The key CTQ was to increase the visibility among the market cluster from less than 30% to 35%. The key action plan that were taken under this project included to know Thana wise TMR/TMS (Trade marketing representative) number of both Airtel & it’s competitors, New town launch activity in rural markets, Launching KRO (Key Retail Outlet) concept.
Speed (Data dominance & capability):
Business Case: Data is one of the fastest growing consumables right now in the telecom industry where the demand is huge. To rightly place Airtel in this market would result to a great leap in revenue as well as customer experience.
Objective of the STRAP: To have dominance in the market in data & increase data usage growth (Data Revenue% to reach from 10% to 15% ).
Sponsor of the Program: ALB member Abhay Sheth who is the head of Brand management of Airtel BD.
Black Belt of the Program: Jinat Laila, Process Manager Commercial, OE.
STRAP Outline
Shobjanta ( well informed CC): The aim of this project was to build well informed customer care representatives who will provide uniform, accurate & complete information to the customers. Also to building their capability across all touch points skills & tools. The name of the project leader is Nilutpola Sharma. The key CTQ was to have percentage increase of VAS FTR (First time resolution), percentage increase in CSI score, percentage increase in internal quiz score. The key action plan that were taken under this project were, VAS training that was segregated & conducted separately, implementation of daily monitoring, Launching Bangla SMS, Quiz on the product within 24 hours of PFS ,100% participation was mandatory. Also, having quiz on VAS , single deactivation code for multiple vendor were implemented.
Smooth Operator: The aim of this project was to create improvement of system availability & accuracy of charging customer as there were a lot of complains previously which were causing serious damage for this brand. The name of the project leader is Jafry Shamim. The key CTQ was to percentage reduction of VAS charging complains. The key action plan that were taken under this project included , implementation of auto reply with correct syntax for wrong key words in GPRS packs, bundle purchases & other VAS, Training on VAS (Based on top interaction), Charging confirmation before activation, establishing Airtel CS (Knowledge Management Portal) availability for ARC agents, Implementation on Start/Stop service through SMS, New services addition on USSD start/stop string, Promotion of Start/Stop service through BTL, creating invalid request in case of low balance to get no pending request.
Mission Possible: The aim of this project was to knowing the demands of customer and provide innovative services to increase revenue by serving better experience to them. The name of the project leader is Makid Hasan. The key CTQ’s were to have percentage increase of VAS Revenue & to have percentage reduction of activation/deactivation problems. The key action plan that were taken under this project included, doing scientific market survey and benchmarking, Innovating new promotional channels, deploying customer profile manager & voice SDP & focusing on first-time and life-enabling services.
STRAP Outline
Aware: The aim of this project was to drive a thorough campaign within the organization to make sure that employees are up-to-date on latest network developments. The name of the project leader is Esmat Ara Sarker. The key CTQ was to have increased score in internal survey score regarding network development. The key action plan that were taken under this project included,
Doing employee survey on network perception and put that as baseline of satisfaction, wallpaper with network info, creating regular E-flyer with network info, Network updated information presentation through all AEC & ARCs & CTO newsletter to all employee.
Project D & R: The aim of this project was to provide POSM and other comprehensive details to the retailers and distributors to fully equip them with necessary network info. The name of the project leader is Moshiur Rahman. The key CTQ’s were to percentage increase of retailers survey score, percentage increase of distributor survey score. The key action plan that were taken under this project included, introducing “Hearing is Believing” program where Thana wiseTMR/ FSE conducted programs in order to create engagement with the retailer- distributors to provide network updates & necessary POSMs. Arranging SMS contest amongst the retailers & creating bulk SMS communication with Thana wise retailers to make them informed about network updates.
Corporate Act: The aim of this project was to satisfy the corporate customers of Airtel with clear and sublime communication on network. The name of the project leader is Rezaul Amin. The key CTQ’s were to have percentage reduction of network complains & to enhance overall corporate satisfaction index. The key action plan that were taken under this project included, providing monthly CEO newsletter to the corporate customers, Regular meeting with Huawei & Erricson in order to stabilize the infrastructure of corporate service in order to keep the corporate client network intact, Incorporating with another program “Enterprise & post paid revamp” as their objective overlaps on serving the corporate clients.
STRAP Outline
There were three projects under this program,
Value: The aim of this project was to provide superior service to the High value (HV) prepaid customers in order to keep them satisfied with Airtel’s specialized service. The name of the project leader is Azmat Ullah Khan. The key CTQ was to have increased Platinum(HV) Prepaid CSI score. The key action plan that were taken under this project included, HV customer flagging in the AEC-ARC- Customer care centers, offering personalized HV service treatment, providing door step service ( SIM delivery/ IR document / recharge), Health Check calls .
Intact: The aim of this project was to retaining the HV prepaid customers & striving for increase this ring more. The name of the project leader is Md. Moneruzzaman. The key CTQ was to enhance the primary SIM using more thus reducing the secondary SIM usage. The key action plan that were taken under this project included, Determining HV customers, Monthly Segmented and aggressive offers through MAMO targeting secondary SIM segment, Offering Gold cards for 30% discount on selective sets, revamping campaign for customer & retails.
Terminator: The aim of this project was to reduce the HV prepaid churn & enhance the site wise performance of those HV prepaid customer area. The name of the project leader is Golam Mohiuddin. The key CTQ’s were to increase the percentage of site wise churn reduction, decrease the percentage of site wise drop in minutes. The key action plan that were taken under this project included, Identifying high churn sites, Field visit on high HV churn sites, Drill down the causes, Bench marking Network quality KPI of high sites, Implementing site wise churn monitoring tool.
Enterprise & Pst-paid Revamp:
Business Case: Airtel has high CMS in the enterprise market but significantly low RMS. Limited packages and solutions are barriers towards catering to these niche corporate customer needs, which is mainly because present IT solutions are not capable of meeting evolving market needs. Additionally, Airtel has no distinct brand positioning in the corporate market or detailed roadmap in their communication process. According to CSMM scores , the CSI score of postpaid had gone up from 43 to 47 , within the time span of Q3 and Q4’11. However, the CSI score of the market leader was 48 in Q4,2011.
Objective of the STRAP: To have growth in Corporate REC base, get higher RMS in enterprise market & reduce corporate value churn.
Sponsor of the Program: Mr. Chris Tobit who is the CEO of Airtel Bangladesh. Black Belt of the Program: Md. Ahmadul Haque, Process Management Manager, OE.
Recommendations
- Although the office environment of Airtel Bangladesh is quite flexible still to compare with the office structures & advantages like GP, Airtel could create recreation zones where its stuffs would have some relaxations during the breaks.
- One of the major drawback that I found in Airtel is lack of internal communication which often causes communication gaps, the impact of which falls on output. In order to have a proper amplified output & greater organizational engagement Airtel should create more internal communication.
- Cross-functional activities of airtel often get fruitless due to lack of willingness of the departments to explain their own jargons. For example, when MKT team works with Engineering team there ENG team is not simplifying the technical terms to MKT team for which that team are failing to understand the situation & bringing about the required output. These issues should be resolved.
- Airtel follows cost-cutting approach according to its policy. But often this cost-cutting approach becomes oversimplified & creates demotivation for the employees. This chould taken care of by prioritizing where to approach this policy where not.