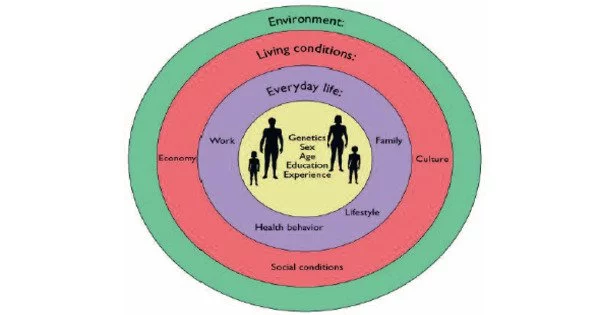
A sociocultural system is the interconnectedness of social and cultural elements within a society. It pertains to a “human population viewed (1) in its ecological context and (2) as one of the many subsystems of a larger ecological system”. It includes the ways in which individuals and groups interact, communicate, and organize themselves within a given cultural context. This system is complex and includes many components such as language, beliefs, values, norms, customs, traditions, institutions, and social structures.
The phrase “sociocultural system” encompasses three ideas: society, culture, and system. A society is a group of organisms of the same species that are interdependent. A culture is the learned behaviors that members of a society share, as well as the material products of those behaviors. The words “society” and “culture” are combined to form the phrase “sociocultural.” The term “system” refers to “a collection of parts which interact with each other to function as a whole”. The term sociocultural system is most likely to be found in the writings of ecological anthropologists.
Key elements of a sociocultural system:
- Language: Language is an important aspect of culture and plays an important role in communication. It not only facilitates information exchange but also reflects a society’s cultural values and perspectives.
- Beliefs and Values: Shared beliefs and values shape sociocultural systems, which guide the behavior and decision-making of individuals within a community. Religious beliefs, moral principles, and cultural norms are examples of these.
- Norms and Customs: Customs are traditional practices or rituals, whereas norms are the unwritten rules that govern behavior within a society. Both contribute to a sociocultural system’s stability and coherence.
- Institutions: Social institutions, such as family, education, religion, government, and the economy, are organized structures that fulfill specific societal functions. They provide a framework for social interactions and contribute to the overall stability of the system.
- Social Structures: These refer to the patterns of relationships and organization within a society. Social structures include family dynamics, social classes, gender roles, and other forms of social organization.
Marvin Harris proposed a universal structure of sociocultural systems in 1979. He referred to infrastructure (production and population), structure (behavioral, such as corporations, political organizations, hierarchies, and castes), and superstructure (mental, such as beliefs, values, and norms).
Sociocultural systems are fluid and change over time. Historical events, technological advancements, globalization, and other external factors all have an impact on them. Understanding the complexities of sociocultural systems is critical for dealing with social issues, fostering cross-cultural understanding, and promoting positive societal development.