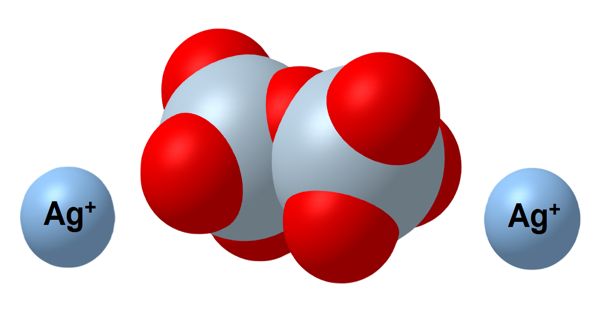
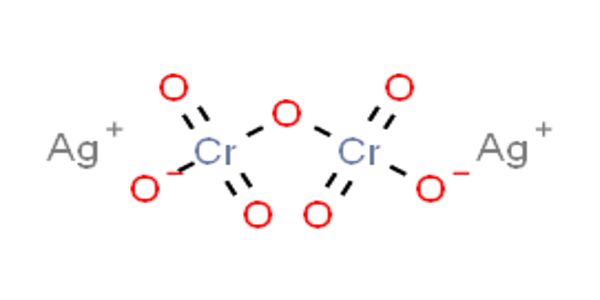
Silver dichromate is a chemical compound with the formula Ag2Cr2O7. It is Solid in state and appears like Ruby Red Powder. It is insoluble in water and decomposes when treated with hot water. It is formed by the combination of the aqueous solution of Potassium dichromate and silver nitrate. Its anion has a charge of -2.
Properties
- State: Solid
- Category: Organic
- Appearance: Ruby Red Powder
- Molar Mass / Molecular Weight : 431.724 g/mol
- Molar Density: 4.77 G/cm3
- Boiling Point: Decomposes
Synthesis
A precipitation reaction is a reaction that yields an insoluble product—a precipitate—when two solutions are mixed. We described a precipitation reaction in which a colorless solution of silver nitrate was mixed with a yellow-orange solution of potassium dichromate to give a reddish precipitate of silver dichromate:
K2Cr2O7 (aq) + 2 AgNO3 (aq) + Ag2Cr2O7 (s) + 2 KNO3 (aq)
Thus precipitation reactions are a subclass of exchange reactions that occur between ionic compounds when one of the products is insoluble. Because both components of each compound change partners, such reactions are sometimes called double-displacement reactions. Precipitation reactions are used to isolate metals that have been extracted from their ores, and to recover precious metals for recycling.
When a colorless solution of silver nitrate is mixed with a yellow-orange solution of potassium dichromate, a reddish precipitate of silver dichromate is produced. Thus precipitation reactions are a subclass of exchange reactions that occur between ionic compounds when one of the products is insoluble.
Applications
Modern photographs use a variety of chemicals to allow the picture to form and be developed. One of the chemicals used is silver chromate. This silver chromate is also used to allow cells to be seen with a microscope by becoming a precipitate inside of the cells, making them visible. This method is called the Golgi method.
Related complexes are used as oxidants in organic chemistry. For instance, tetrakis(pyridine)silver dichromate, [Ag2(py)4]2+[Cr2 O7]2-, is used to convert benzylic and allylic alcohols to corresponding carbonyl compounds.
Information Source: