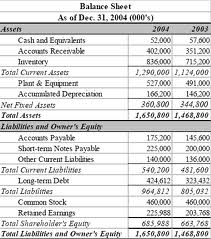
Rules of Preparation of Balance Sheet
A balance sheet allows you to see at a glance what your company’s assets and liabilities are. The balance sheet is basically a summary of what you own and what you owe. Assets, liabilities and owner’s capital are listed as of a certain date, usually at the end of a month, quarter or fiscal year. Your balance sheet gives you a way to determine the value of your business at any particular time.
Preparation of balance sheet of company is very necessary, because Indian Company law 1956 gives strict instruction about the format of balance sheet of a company. A company can make balance sheet according to the form given in Part I of schedule VI of company law 1956. A company can also make balance sheet summary form, but it has to attach its schedule in which explanation of different components are given. We are explaining different components of balance sheet of company which will be helpful for students to prepare balance sheet of company.
[* Remember the form of balance sheet under Section 211]
You should remember balance sheet and its all components thoroughly. It can be made either horizontal or vertical form. But total of assets should be equal to total of liabilities. Here, I am explaining these components.
Assets Side of Balance Sheet
- Assets are written in right side of company’s balance sheet. In these assets, we include.
1.
- 1. Fixed AssetsWe will show all fixed assets which are purchased and used in business. This is the long term expenditure of company. In these assets, we will include following.I) LandII) BuildingIII) Plant and MachineryIV) Furniture and FixtureV) Leasehold assetsVI) Development of propertyVII) VehiclesVIII) Live stocksIX) Railway sidingsX) EquipmentsWe also include intangible assets in fixed assets head. Following are the main examples of intangible assets.I) Goodwill
II) Patents
III) Trade marks and designDepreciation is charged on every fixed asset except land, because value of land will increase after some time. Here, students are given advice that they should calculate the value of net fixed assets, if different fixed assets are purchased or sold during the year. The following table will be the part of working note.
2. Treatment of Investment in balance sheetInvestment is outflow of fund for getting interest or dividend earning. So, it is the asset of company and will include in assets side. The following are the main investments.a) Investment in Government or trust securities.b) Investment in Shares, debentures or bondsThe following points must be kept in mind while you are showing investment in balance sheet.i) Investment in fully paid up shares must be shown separately from investment in partly paid up shares.ii) Investment in the form of shares in subsidiary company must be shown separately from investment in any other company.c) Investment in immovable properties.d) Investment in the capital of partnership firms.Investment will be shown on cost or market value which is less.3. Treatment of current assets , loan and advances in balance sheetA) Current assetsCurrent assets will be shown in separate head and following components will be included in it.i) Stock in tradeii) Work in progressiii) Stock of stationaryiv) Stock of loose toolsv) Stock of stores and spare partsvi) Sundry debtors less provision for doubtful debtsvii) Cash in handviii) Bank balancea) With schedule bankb) With other banksB) Loan and AdvancesThe amount which is given by company to others in the form of loan or advances will be shown in asset side. Followings are its main examples.a) Advance and loan to subsidiary companyb) Advance and loan to partnership firmc) Bill of exchange / Bill receivablesd) Advance expenses paide) Outside incomes.4. Miscellaneous expendituresExpenses which are not written off will be shown in asset side of balance sheet. There is no market value of these expenses. Examples are given below.i) Preliminary expensesii) Commission or brokerage of subscription of shares ordebenturesiii) Discount allowed on issue or shares and debenturesiv) Interest paid out of capital during constructionv) Development expenditure5. Profit and Loss AccountIf company suffers net loss after adjusting all reserves, then it will be shown in asset side. This amount can be also deducted from reserves in liabilities side. That time, we will not show it in asset side.
Liabilities Side of Balance Sheet
Liabilities are written in left side of company’s balance sheet. In these liabilities, we include.1. Share CapitalIn share capital of company, we have to show authorized capital, subscribed capital, called up capital and paid up capital. For calculating paid up capital, we will deduct calls unpaid and add original paid up amount offorfeited shares.
2. Reserves and SurplusFollowing reserves will be shown in liabilities side of balance sheet of company.i) Capital reservesii) Share premium accountiii) Other reservesiv) Surplus balance in profit and loss account after providingdividend, bonus or reserves.v) Sinking fund3. Secured LoanIf any loan is taken by company after keeping any asset as security, then it will be shown in secured loan head. Its detail is given below.i) Debenturesii) Loan and advances from subsidiariesiii) Other loan and advancesiv) Interest payable on secured loan4. Unsecured loanFollowing will be the unsecured loan.i) Fixed deposits of publicii) Short term loans and advancesiii) Other loans5. Current Liabilities and ProvisionsAll liabilities which is payable within one year, will be included in current liabilities head.A) Current Liabilitiesi) Acceptance or bill payablesii) Sundry creditorsiii) Interest payable other than on loaniv) Outstanding expendituresB) Provisionsi) Provisions for taxationsii) Proposed dividendiii) Provision for provident fundiv) Provision for insurance, pension and other staff benefit schemesv) Other provisions6. Contingent liabilitiesThese types of liabilities will not be shown in balance sheet. But a simple footnote is made for its detail. Following may be the contingent liabilities of company.i) Claims against the company not acknowledge as debtsii) Uncalled liability on shares paidiii) Areas of fixed cumulative dividendsiv) Any other contingent liability of company