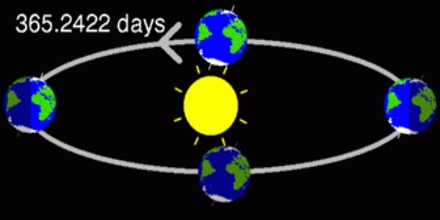
The Sun’s position relative to Vernal Equinox is important for determining the seasons and the calendar. A major function of the calendar was for agriculture. Solar motion on the ecliptic is not uniform (due to the Earth’s elliptical orbit), hence seasonal lengths are different. The mean tropical year, i.e. the mean duration for the Sun to pass though the same point on the ecliptic twice, is 365.242 190 419 days (epoch 2000). A good approximation is 365 + 97/400 = 365.2425 days. This leads to 97 leap years in every 400 years (Gregorian calendar).
Relation between Solar motion and the Calendar