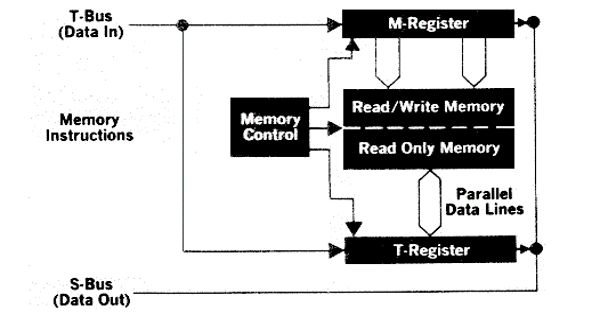
Read-write memory (RWM) is computer memory that can be read from and written to. It is a type of computer memory that may be relatively easily written to as well as read from, that is, using electrical signaling normally associated with running software, and without any other physical processes (unlike ROM or “read-only memory” and distinct from EEPROM). This type of memory can be contrasted with read-only memory, which cannot be modified after it is written. The purpose of this type of memory can be to permanently store information for later use, such as is the case with a CD-RW, or it can be to provide an area of fast access to information that has been compiled or loaded, as is the case with RAM chips.
Read-write memory is a type of electronic storage used by computers and other devices that can have information stored on it and, subsequently, can have that same information retrieved later.
The related term RAM (for “random access memory”) means something different; it refers to memory that can access any memory location in a constant amount of time. In general, the use of read-write memory represents the need for users to continually update the data that is held on hardware storage devices. There are several physical forms of read-write memory, such as computer random access memory (RAM) chips, hard drives, and rewritable compact disks (CD-RWs) to name a few.

The term might also refer to memory locations having both read and write permissions. Both of these contrast with another, more obscure, type of memory called write-only memory, which is very narrowly applied to hardware setups. In modern computer systems using memory segmentation, each segment has a length and set of permissions (for example, read, write, execute) associated with it. Having read-write memory design makes devices much more valuable to users, and adds more functionality to technologies.
Types
Read-write memory is composed of either volatile or non-volatile types of storage. It comes in all kinds of physical setups. A computer holds many types of storage that can Read-write memory and be in many different physical sizes and forms.
From an internal or external hard disk drive to rewritable CDs or small flash drives that connect over USB, users of today’s modern computer systems can house readable and writable data in many different kinds of data storage destinations. Typically read-write speeds are limited to their bandwidth or have mechanical limitations of either rotation speeds and arm movement delays for storage types such as Cloud Storage, Hard Disk Drive or CD-RWs, DVD-RWs, SD cards, Solid State Drive, SRAM, and DRAM, or other integrated circuitry. In addition to physical data storage devices, new technologies like network virtualization and cloud hosting have given users even more options for storing and retrieving data that can be changed or amended as needed.
Information Source: