Pyroglutamic acid (also known as PCA, 5-oxoproline, pidolic acid) is a ubiquitous but understudied natural amino acid derivative in which the free amino group of glutamic acid or glutamine cyclizes to form a lactam. It is a derivative of the amino acid glutamic acid. The names of pyroglutamic acid conjugate base, anion, salts, and esters are pyroglutamate, 5-oxoprolinate, or pidolate. It has unique structural, chemical, and biological properties and occurs naturally in a range of biological systems.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C5H7NO3
- Molar mass: 129.115 g·mol−1
- Melting point: 184 °C (363 °F; 457 K)
- log P: −0.89
- Acidity (pKa): −1.76, 3.48, 12.76
- Basicity (pKb): 15.76, 10.52, 1.24
- Isoelectric point: 0.94
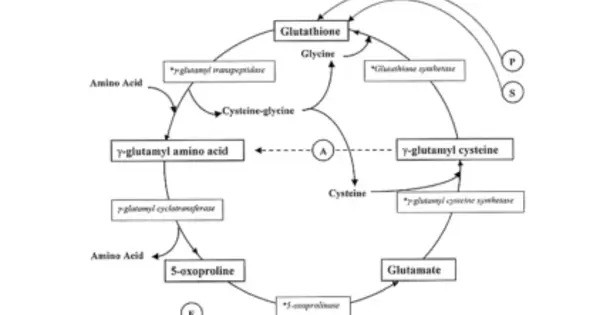
It is a metabolite in the glutathione cycle that is converted to glutamate by 5-oxoprolinase. Pyroglutamate is found in many proteins including bacteriorhodopsin. N-terminal glutamic acid and glutamine residues can spontaneously cyclize to become pyroglutamate, or enzymatically converted by glutaminyl cyclases. This is one of several forms of blocked N-termini which present a problem for N-terminal sequencing using Edman chemistry, which requires a free primary amino group not present in pyroglutamic acid. The enzyme pyroglutamate aminopeptidase can restore a free N-terminus by cleaving off the pyroglutamate residue.
Formation and Metabolism
- Endogenously Formed from: Spontaneous cyclization of glutamic acid or glutamine, particularly in acidic or high-heat conditions. Intermediate in the γ-glutamyl cycle, involved in glutathione metabolism.
- Enzyme Involvement: Glutathione synthetase deficiency or 5-oxoprolinase deficiency can lead to accumulation of pyroglutamic acid.
- Excretion: Normally excreted in small amounts in urine. Elevated levels detected in metabolic disorders or drug-induced toxicity (e.g., paracetamol/acetaminophen overuse).
Biological Roles and Relevance
Neurobiology: Pyroglutamate may act as a neuromodulator and is associated with neurotransmission due to its structure and occurrence in CSF.
Skin Hydration: Sodium pyroglutamate (NaPCA) is used in cosmetics for its moisture-retaining properties.
Pathology Marker: Elevated in:
- Inborn errors of metabolism (e.g., pyroglutamic aciduria)
- Drug-induced metabolic acidosis
- Severe oxidative stress