Palladium is a commonly used catalyst for the formation of C-C, C-O, and C-N bonds in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Pseudo palladium (RhAg) is a binary alloy consisting of equal parts of rhodium (atomic number 45) and silver (atomic number 47) created using nanotechnology to create a far more homogeneous mixture than might be possible using more conventional methods. Palladium cross-coupling reactions of α-haloselenophenes are a useful tool for the preparation of selenophene-containing copolymers. This alloy exhibits properties of the intervening element palladium (atomic number 46).
Pseudo palladium is a binary alloy consisting of equal parts of rhodium and silver created using nanotechnology to create a far more homogeneous mixture than might be possible using more conventional methods.
Characteristics
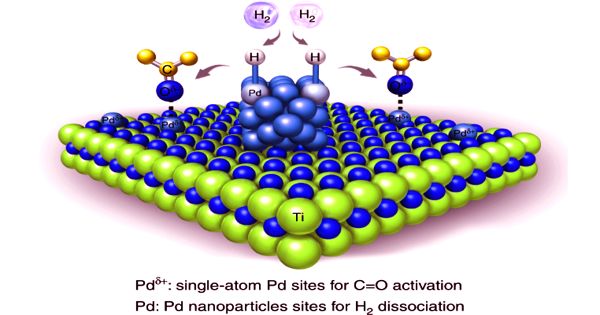
Palladium is one of the six platinum group metals and possesses strong catalytic activity. The new alloy has similar properties to palladium, which is used as a catalyst to cleanse exhaust gas and absorbs large quantities of hydrogen. Nano-structured palladium (Pd) is advantageous in the sensitive detection of hydrogen because of its large surface area. However, the formation of Pd nanostructure is not easy but requires expensive and complicated processes.
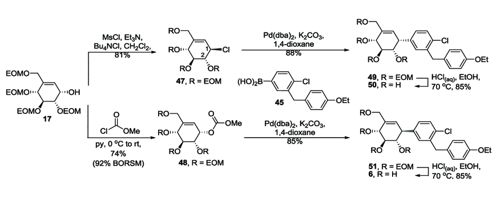
Preparation of pseudo C glycosides via palladium-catalyzed allyl aryl coupling reaction
Palladium is a lustrous silver-white metal. It has a face-centered cubic crystalline structure, at ordinary temperatures, it is strongly resistant to corrosion in air and to the action of acids. Rhodium, palladium, and silver have 45, 46, and 47 electrons, respectively, numbers that determine their chemical characterizations. Demand for palladium is high owing to its uses in electrical equipment, dental materials, and automobile catalysts.
“The orbits of the electrons in the rhodium and silver atoms probably got jumbled up and formed the same orbits like those of palladium,” Kitagawa said.
Applications
Palladium is used extensively in jewelry-making in certain alloys called “white gold.” It may be alloyed with platinum or substituted for it. The alloy has similar properties to palladium, which is used in cars’ emissions-reducing catalytic converters as well as in computers, mobile phones, flatscreen TVs, and dentistry instruments.
Hydrogen storage is cited as one potential use, however, according to researchers, the pseudo palladium alloy has only one half of palladium’s hydrogen storage capacity.
Information Source: