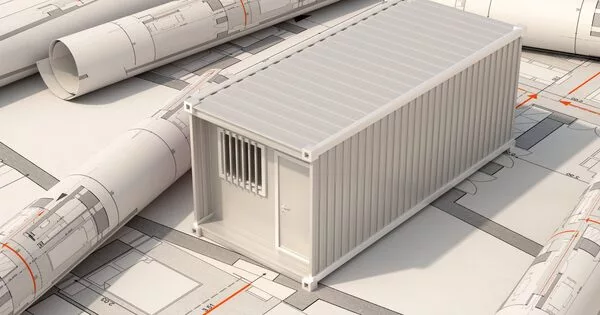
A prefabricated building, also known as a prefab, is one that is manufactured and built using prefabrication. It is a structure that is built off-site in a factory or manufacturing facility and then transported to the final assembly location. It is made up of factory-made components or units that are transported and assembled on-site to form the entire structure. Prefabricated buildings are built with standardised components manufactured in a controlled environment, ensuring consistent quality and efficiency.
The process of constructing a prefabricated building involves the following steps:
- Design: The structure is designed to meet the client’s specific needs and specifications. Architects and engineers create detailed plans that consider size, layout, materials, and functionality.
- Manufacturing: A factory or manufacturing facility produces the building components. Walls, floors, roofs, doors, windows, and other structural elements are all included. Steel, wood, concrete, or a combination of these materials are used to construct these components.
- Transportation: The components are transported to the construction site after they have been manufactured. Transportation can involve trucks, rail, or shipping containers, depending on the size of the building. For ease of assembly, the components are carefully packaged and labelled.
- Assembly: On-site, the prefabricated building components are assembled according to the predetermined design and plans. The components are typically connected using bolts, screws, or welding, depending on the construction materials used. Cranes or other lifting equipment may be required to lift and position the components.
- Finishing: After the main structure is assembled, the interior and exterior finishes are applied. This includes electrical and plumbing installations, insulation, interior walls, flooring, and painting. The finishing process is similar to that of traditional construction methods.
Prefabricated buildings offer several advantages over traditional construction methods:
- Speed: Prefabricated buildings can be constructed much faster compared to traditional construction. Since the components are manufactured off-site, construction can proceed simultaneously at the site, reducing the overall construction time.
- Cost-effective: Prefabricated buildings can be more cost-effective than traditional construction, as the manufacturing process allows for efficient use of materials and reduced labor costs. The controlled environment in the factory also helps minimize waste.
- Quality control: Prefabricated buildings are constructed under controlled conditions, ensuring consistent quality throughout the building process. The use of standardised components and stringent quality control measures results in greater precision and dependability.
- Flexibility: Prefabricated buildings are designed to be easily assembled and disassembled, allowing for mobility and expansion. The modular nature of these buildings allows for customization and future modifications based on the client’s changing needs.
- Sustainability: Sustainable design principles, such as the use of energy-efficient materials and systems, are frequently incorporated into prefabricated buildings. When compared to traditional construction, the controlled manufacturing process can also reduce waste and have a lower environmental impact.
Residential homes, office buildings, schools, healthcare facilities, retail spaces, and temporary structures such as site offices or emergency shelters are all examples of prefabricated buildings. Prefabricated construction has become a popular choice in many construction projects due to its variety of design options and versatility.