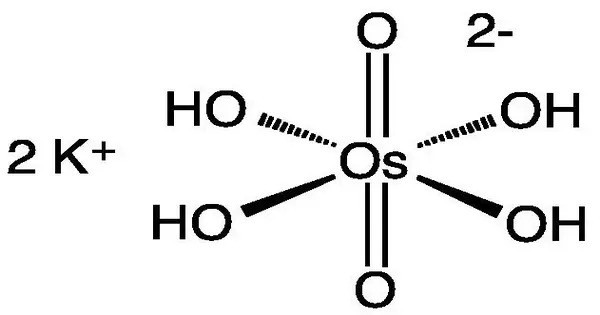
Potassium osmate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2[OsO2(OH)4]. It is a potassium salt of osmium tetroxide (OsO₄), where osmium is in its +8 oxidation state. This compound is typically used in organic chemistry and biochemistry, especially for its role as a reagent in osmium tetroxide-related reactions.
This diamagnetic purple salt contains osmium in the VI (6+) oxidation state. When dissolved in water a red solution is formed. When dissolved in ethanol, the salt gives a pink solution, and it gives a blue solution when dissolved in methanol. The salt gained attention as a catalyst for the asymmetric dihydroxylation of olefins.
Synthesis
Potassium osmate can be synthesized by the reaction of osmium tetroxide (OsO₄) with potassium hydroxide (KOH) or potassium carbonate (K₂CO₃). It is used primarily in organic chemistry as a reagent for selective oxidation reactions, such as in the osmylation of alkenes to form vicinal diols. This process is especially useful for forming diol compounds in organic synthesis.
Properties
- Chemical formula: H4K2O6Os
- Molar mass: 368.42
- Appearance: purple solid
- Stability: Potassium osmate is relatively stable in ambient conditions but should be handled with care, as osmium compounds can be toxic and some can be volatile under certain conditions. It may decompose under extreme conditions.
Preparation
The compound was first reported by Edmond Frémy in 1844. Potassium osmate is prepared by reducing osmium tetroxide with ethanol:
2 OsO4 + C2H5OH + 5 KOH → CH3CO2K + 2 K2[OsO2(OH)4]
Alkaline oxidative fusion of osmium metal also affords this salt.
Occurrence
Potassium osmate does not naturally occur in large quantities in nature. It is a synthetic compound typically produced in laboratory or industrial settings, especially in reactions involving osmium. Osmium is a rare and dense metal, and its compounds are usually prepared by reacting osmium tetroxide with alkali metals or their hydroxides.
Applications
Potassium osmate is important in organic chemistry as a reagent in reactions such as:
- Osmylation: It is used in the osmium tetroxide catalyzed hydroxylation of alkenes. Potassium osmate can be used to form osmylation products in the synthesis of diols (two hydroxyl groups on a molecule).
- Synthesis of Osmium Complexes: Potassium osmate can be used as a precursor to other osmium compounds and complexes used in catalysis.
- Catalysis: It has applications in asymmetric synthesis and other catalytic processes, particularly in fine chemical and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Safety Considerations
Like osmium tetroxide, potassium osmate is toxic and potentially harmful. Osmium tetroxide is highly volatile and can cause severe respiratory, skin, and eye irritation. Special care must be taken when handling these compounds, especially in well-ventilated spaces or fume hoods.