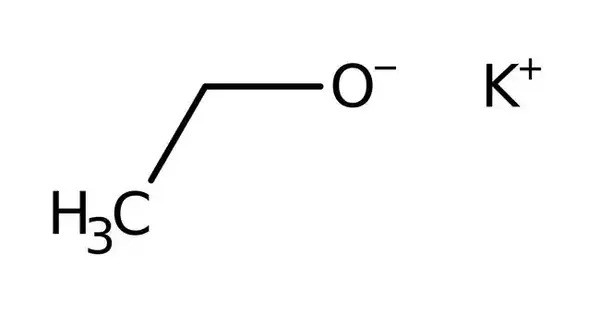
Potassium ethoxide, also known as potassium ethanolate, is an off-white or yellow powder with the chemical formula of C2H5KO. It is a strong organic base and alkoxide, widely used in organic synthesis. It is the potassium salt of ethanol, formed when potassium metal reacts with absolute ethanol, releasing hydrogen gas. Due to its strong basicity and nucleophilic nature, it serves as a powerful reagent in elimination reactions (E2 mechanism), esterifications, and the preparation of fine chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals.
Potassium ethoxide contains an ethoxide ion, the conjugate base of ethanol, which makes these compounds strongly basic. It hydrolyzes to yield ethanol and potassium hydroxide. This compound is highly reactive, particularly with moisture and carbon dioxide, which can degrade it into ethanol and potassium carbonate.
Properties
In its pure form, potassium ethoxide appears as a white to yellowish powder or crystalline solid. It is soluble in ethanol and other organic solvents but reacts violently with water, producing ethanol and potassium hydroxide.
- Chemical formula: C2H5KO
- Molar mass: 84.159 g·mol−1
- Appearance: Yellow or Off-White Powder
- Density: 0.894 g/mL
- Melting point: 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K)
- Solubility in water: Reacts
- Odor: Alcohol-like due to its strong reactivity with ethanol.
- Reactivity: Strong base and a powerful nucleophile, often used in organic synthesis for deprotonation and elimination reactions (e.g., E2 reactions).
- Stability: Very moisture-sensitive; decomposes in air or when exposed to water, releasing flammable ethanol.
- Flammability: Highly flammable due to ethanol vapor formation upon hydrolysis.
Occurrences
Potassium ethoxide does not occur naturally; it is a synthetic compound. It is typically prepared by reacting potassium metal with absolute ethanol, producing potassium ethoxide and hydrogen gas. The compound is mainly encountered in laboratories and chemical industries, especially in organic and pharmaceutical synthesis. It serves as a strong base for condensation reactions (like Claisen condensation), alkylation, and the preparation of various organic intermediates.
Uses
Potassium ethoxide is used as a strong base, similar to sodium and potassium methoxides, and potassium tert-butoxide. Catalytic amounts of potassium ethoxide in ethanol can be used to perform transesterification reactions that yield ethyl esters. Sodium or potassium ethoxide is also a suitable base for the malonic ester synthesis where diethyl malonate is used, since any transesterification reaction does not result in ester scrambling.
Safety
Potassium ethoxide is stable, but also both flammable and corrosive. The compound reacts vigorously with water. If the compound comes into contact with damp air, it may lead to the heating and ignition of the solid powder. It must be kept separated from air, moisture, water, acids, oxidizing agents, and reducing agents. It can also cause severe skin burns.
Potassium ethoxide must be handled under dry, inert conditions (like nitrogen or argon atmosphere) because of its sensitivity to air and moisture. It is flammable and corrosive, causing burns upon skin contact and irritation to the respiratory system if inhaled. Storage typically requires tightly sealed containers, away from water, acids, and oxidizing agents.