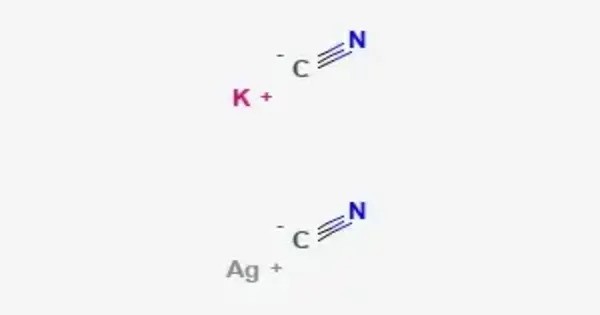
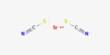
Potassium dicyanoargentate is an inorganic compound with the formula KAg(CN)2. A white solid, it is the K+ salt of the linear coordination complex [Ag(CN)2]−. It is a coordination complex of silver with cyanide, widely used in silver electroplating due to its solubility and stability compared to AgCN. It forms upon treatment of virtually any silver salt with two equivalents of potassium cyanide. It is highly toxic because of cyanide, requiring careful handling, but its importance lies in metallurgy, electrochemistry, and analytical chemistry.
Properties
- Chemical formula: KAg(CN)2
- Molar mass: 199.001 g/mol
- Appearance: White crystals
- Density: 2.36 g/cm3
- Solubility in water: Soluble
- Solubility: Insoluble in acids
- Refractive index (nD): 1.625
Physical Properties
- Appearance: White to colorless crystalline solid.
- Solubility: Soluble in water (due to ionic nature).
- Stability: Stable under normal conditions, but decomposes when heated strongly, releasing toxic cyanide fumes.
- Odor: Generally odorless, though may release faint almond-like smell if decomposition releases HCN.
Chemical Properties
- A cyanide complex of silver, which is more stable than free silver cyanide.
- Acts as a source of silver ions in cyanide form, commonly used in electrochemistry.
- Can form related complexes with alkali metals (e.g., Na[Ag(CN)₂]).
- Toxic due to the presence of cyanide.
Preparation
Prepared by dissolving silver(I) cyanide (AgCN) in aqueous potassium cyanide (KCN):
AgCN+KCN→K[Ag(CN)2]
This reaction stabilizes silver in solution by forming the soluble dicyanoargentate complex.
Reactions
- KAg(CN)2 is significant adventitious product of gold mining using cyanide as an extractant.
- It can be used in silver plating, as a bactericide, and in the manufacture of antiseptics.
- It forms a variety of coordination polymers, a property that exploits the bridging tendency of the cyanide ligand.
Applications
- Electroplating: Used in silver electroplating baths, as it provides a soluble and stable source of silver ions. Ensures smooth and uniform silver coatings on metals.
- Analytical Chemistry: Utilized in argentometric titrations (volumetric methods involving silver salts). Forms basis for certain cyanide complexation studies.
- Photography (historically): Related cyanide complexes were used in photographic processing, though less common today.