Polyurethane foams are materials with a low weight-to-strength ratio, desirable insulating properties, and a strong tendency for energy absorption. Polyurethane Foam is a polymer composed of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. It is best known for supporting our body for a large part of the day, in mattresses, upholstered furniture, and car seats. While most polyurethanes are thermosetting polymers that do not melt when heated, thermoplastic polyurethanes are also available. What is sometimes less known is that we enjoy the benefits of hundreds of polyurethane foam articles without even noticing. It has been widely used in active high-volume air samplers due to their high retention capacity of organic pollutants.
Polyurethane foam is one component, curing with moisture in the air, expanding while curing, semi-rigid in aerosol form for installation, grouting, and insulation material.
Polyurethane polymers are traditionally and most commonly formed by reacting a di- or triisocyanate with a polyol. Flexible polyurethane foams are prepared from basically the same raw materials as polyurethane elastomers. Since polyurethanes contain two types of monomers, which polymerize one after the other, they are classed as alternating copolymers. Flexible PUR foams can be categorized according to their chemical structure or according to their production method.
Both the isocyanates and polyols used to make polyurethanes contain, on average, two or more functional groups per molecule. The chemical structure is influenced by the choice of the polyol, polyether or polyester, and by the choice of the isocyanate, TDI or MDI.
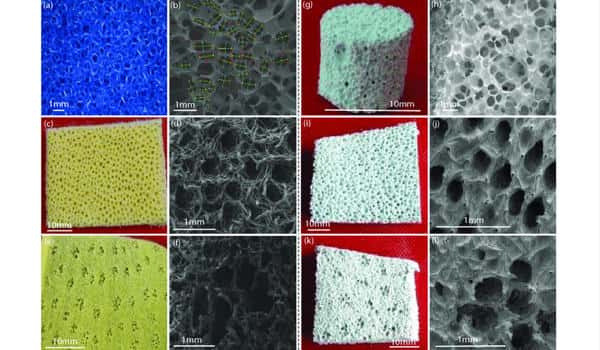
Polyurethane is a leading member of the wide-ranging and highly diverse family of polymers or plastics. The stabilization of foam during manufacture of polyurethane foam (PUF) was the first, and remains the largest single commercial application of silicone surfactants. PU foams are formed by the reaction between an isocyanate prepolymer and a polyol in the presence of a blowing agent, and an amine.
Types
- Flexible Polyurethane Foam – It is used as cushioning for a variety of consumer and commercial products, including bedding, furniture, automotive interiors, carpet underlay and packaging. It is light, durable, supportive and comfortable.
- Rigid Polyurethane Foam – It create one of the world’s most popular, energy-efficient and versatile insulations.
Polyurethanes are used in the manufacture of high-resilience foam seating, rigid foam insulation panels, microcellular foam seals and gaskets, spray foam, durable elastomeric wheels and tires, automotive suspension bushings, electrical potting compounds, high-performance adhesives, surface coatings and sealants, synthetic fibers (e.g., Spandex), carpet underlay, hard-plastic parts (e.g., for electronic instruments), condoms, and hoses. Its applications are virtually endless, ranging from small but essential items such as sponges in the kitchen, medical dressings to large filters and soundproofing systems that keep our environment clean and quiet. PU foam is also the most important insulating material for water heaters, both domestic and industrial. Water heaters can make use of gas, electrical or solar heating systems. New regulations are developing worldwide in order to improve the energy efficiency.
Information Source: