Pelargonic acid, commonly known as nonanoic acid, is a carboxylic acid chemical that is found in nature. It can be found in the form of esters in the oil of pelargonium. It is a nine-carbon fatty acid and an organic molecule with the structural formula CH3(CH2)7CO2H. Nonanoic acid is a nine-carbon saturated fatty acid that occurs naturally. Herbicides are made from the ammonium salt version of nonanoic acid. It acts by removing the plant’s waxy cuticle, producing cell disruption, cell leakage, and desiccation death.
Pelargonic acid (Nonanoic Acid) is an oily, colorless liquid with a rotten odor. In water, it’s practically insoluble, but it’s extremely soluble in organic solvents. It is frequently used in combination with glyphosate, a non-selective herbicide, to achieve a fast burn-down effect in the suppression of weeds in turfgrass. It’s also an effective antifungal agent, inhibiting pathogenic fungi’s spore germination and mycelial growth. Flavorings can be made from its synthetic esters, such as methyl nonanoate.
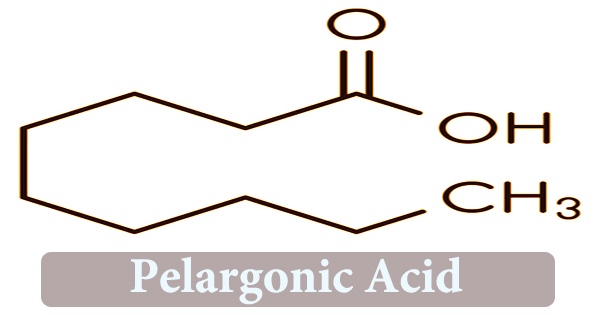
Nonanoic acid is a C9 straight-chain saturated fatty acid found in the oil of pelargonium as esters. It’s an antifungal agent that’s also used as a herbicide and in the manufacture of plasticizers and lacquers. Pelargonates or nonanoates are the esters and salts of pelargonic acid. The pelargonium plant’s oil includes esters of the acid, so the acid is named after it. It can also be utilized in the manufacture of plasticizers and lacquers. It has the potential to be utilized to treat seizures as well.
It functions as an antifeedant, a plant metabolite, a metabolite from Daphnia magna, and an algal metabolite. It has a refractive index of 1.4322, a critical point of 712 K (439 °C), and a pressure of 2.35 MPa. Pelargonic acid (nonanoic acid) is manufactured industrially with azelaic acid by ozonolysis of oleic acid.
CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7CO2H + 4O → CH3(CH2)7CO2H + HO2C(CH2)7CO2H
This acid has a greasy, distinctive odor as well as an unpleasant taste. It can be made by oxidizing methylnonyl ketone, oxidizing oleic acid, or making malonic ester from heptyl iodide. Pelargonic acid can also be made in a two-step process that starts with 1,3-butadiene linked dimerization and hydroesterification. This step produces a doubly unsaturated C9-ester, which can be hydrogenated to give esters of pelargonic acid.
2 CH2=CH-CH=CH2 + CO + CH3OH → CH2=CH(CH2)3CH=CHCH2CO2CH3
CH2=CH(CH2)3CH=CHCH2CO2CH3 + 2 H2 → CH3(CH2)7CO2CH3
It is a medium-chain saturated fatty acid with a straight chain. It is a nonanoate conjugate acid that comes from a nonane hydride. Pelargonic acid is found naturally as esters in pelargonium oil. In a reactor, an 18-inch-high body of liquid containing a 35 percent (by weight) solution of technical (95%) oleic acid in n-propanol is kept at 86°C. The solution also has 0.042 percent by weight of cobalt in the form of cobalt naphthenate dissolved in it. For 72 hours, very fine bubbles of air are passed into and through the solution from the bottom of the reactor at a rate of around 0.3 cubic feet per minute per square foot, measured under standard circumstances.
After passing through an ice water reflux condenser, the gases leaving the reactor are released to the atmosphere. The reaction mixture is separated into its components at the end of the 72-hour period. It is discovered that the process has consumed 60% of the oleic acid. Pelargonic acid is also utilized in the manufacture of lacquers and plasticizers. In some pepper sprays, the derivative 4-nonanoylmorpholine is used. Ammonium pelargonate, the ammonium salt of pelargonic acid, is a herbicide.
It’s frequently combined with glyphosate, a non-selective herbicide, for a speedy burn-down action in turfgrass weed management. Lacquers, plastics, medicines, synthetic scents and flavorings, fuel additives, flotation agents, lubricants, and vinyl plasticizers are just a few of the products made with this acid. Nonanoic acid is used as a topical bactericide and fungicide in pharmaceutical products. Herbicides also include it. It acts by removing the plant’s waxy cuticle, producing cell disruption, cell leakage, and desiccation death.
Information Sources: